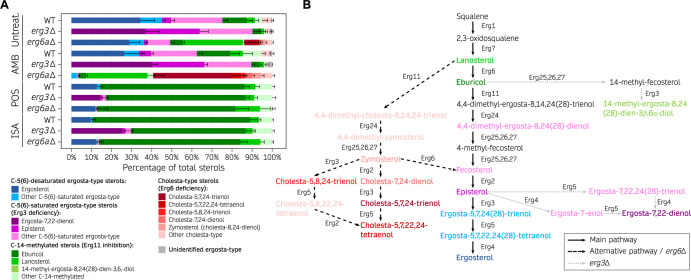
Fig 5.
Ergosterol composition upon exposure to first-line mucormycosis treatments is altered by Erg3 and Erg6a deficiencies. (A) Percentage of total sterols in M. circinelloides wildtype (WT), erg3Δ, and erg6aΔ strains when exposed to different antifungal treatments (amphotericin B, posaconazole, and isavuconazole) and untreated RPMI cultures, represented in a stacked bar plot. Mean and SD (only upper bound is shown) values were determined from six replicates in the WT strain; for each mutation and condition, two independently generated mutants were tested in triplicate (total of 6 replicates). Sterols are classified into four main categories that reflect the expected end products from the main ergosterol pathway [C-5(6)-desaturated sterols], Erg3 deficiency [C-5(6)-saturated sterols], Erg6 deficiency (cholesta-type sterols), and Erg11 inhibition due to azole exposure (14-methylated sterols). Within each category, the most abundant sterols are color-coded to facilitate visualization. (B) Model of the ergosterol biosynthetic pathway in Mucorales. The main pathway is depicted by straight, black arrows. Alternative pathways that are relevant in erg3 (dashed, black arrows) or erg6a deletions (dotted, gray arrows) are also shown. For better illustration, sterol compounds are classified and color-coded as in (A).