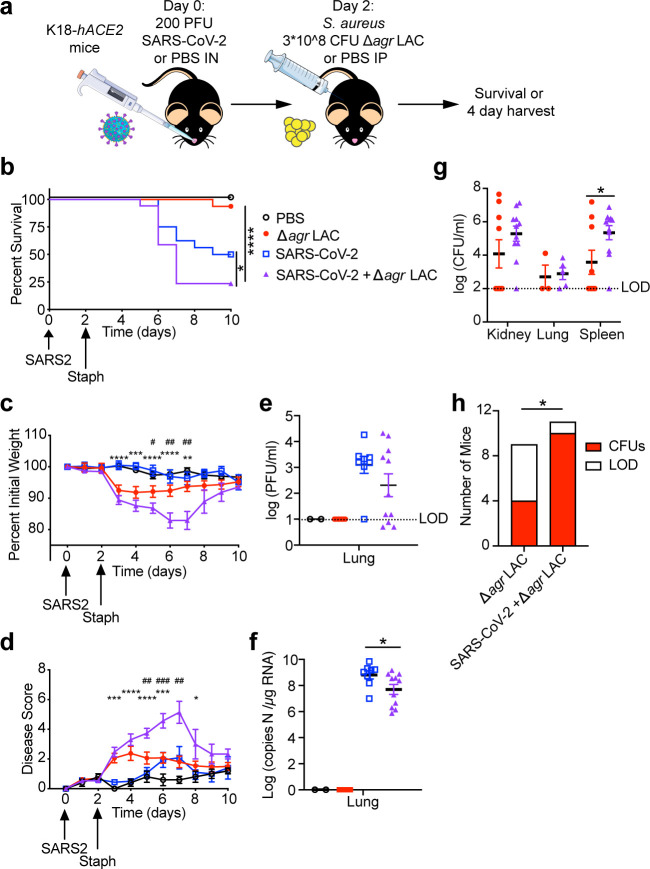
Fig 5.
SARS-CoV-2 increases susceptibility to S. aureus in mice. (a) Schematic of coinfection experimental design. Survival (b), weight loss (c), and disease score (d) of mice infected with the indicated pathogens (15–17 mice per group, 5 mice in the PBS group). Viral burdens in lungs as determined by plaque assay (e), and qPCR (f) at 4 days post-infection. (g) Bacterial burdens of S. aureus in the indicated organs by CFU at 4 days post-infection. (h) Number of mice that were colonized with S. aureus by 4 days post-infection in any organ (CFUs) or not (LOD) (h). Error bars represent mean +/- SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. b, Mantel-cox test, c, d, Mann-Whitney test, g, Student’s t-test, h, Fisher’s exact test. In panels c and d, * indicates a difference between the SARS-CoV-2 infected group and the coinfected group,and # indicates a difference between the S. aureus infected group and the coinfected group.