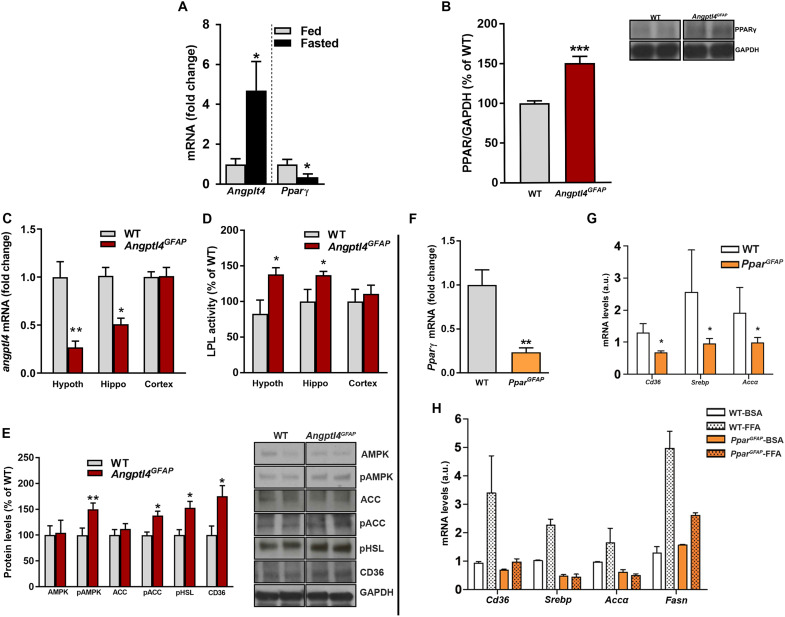
Fig. 4. ANGPTL4 regulates the expression of PPARγ.
(A) Angptl4 and Pparγ mRNA levels from hypothalamic astrocytes of fed and fasted WT mice (n = 4 mice per group). (B) Quantification and representative blots (from the same film) showing the levels of PPARγ in MBH of Angptl4GFAP mice and their littermate controls (n = 5 mice per group). (C) Angptl4 mRNA levels and (D) LPL activity in the hypothalamus, hippocampus, and cortex of Angptl4GFAP mice and their controls (n > 7 mice per group). (E) Quantification and representative blots (from the same film) showing the levels of AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase), pAMPK, ACC (acetyl-CoA carboxylase), pACC, pHSL (phosphorylated hormone-sensitive lipase), and CD36 in the MBH of Angptl4GFAP mice and their controls (n = 5 mice per group). (F) Pparγ mRNA levels from hypothalamic astrocytes of PparGFAP mice and their controls (n = 4 samples per group). (G) Cd36, Srebp, and Acc mRNA levels from hypothalamic astrocytes of PparGFAP and their control mice (n = 4 samples per group). a.u., arbitrary units. (H) Cd36, Srebp, Acc, and Fasn mRNA levels from primary cultures of hypothalamic astrocytes of PparGFAP and their control mice treated with bovine serum albumin (BSA) or free fatty acid (FFA) (n = 4 or 5 samples per group). Data are presented as means ± SEM. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, and ***P ≤ 0.001 as determined by two-tailed t test.