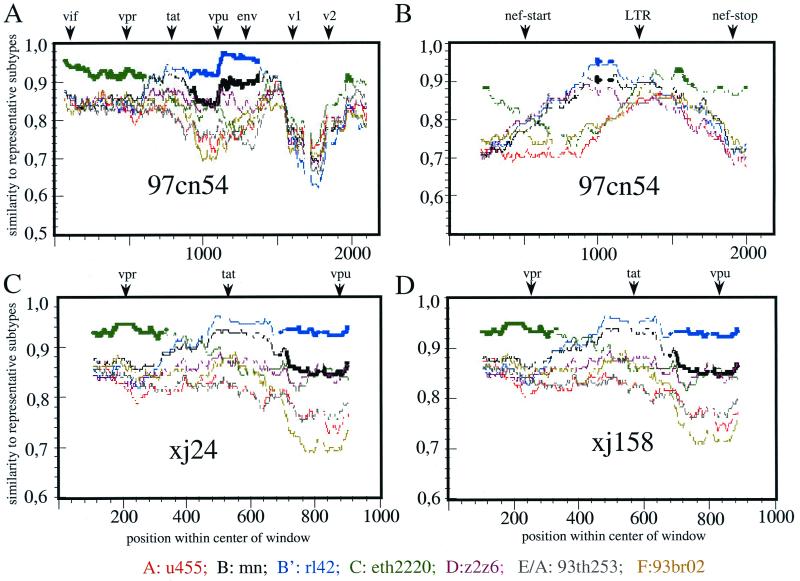
FIG. 4.
RIP analysis (version 1.3) of different regions of 97cn54 (window size, 200; threshold for statistical significance, 90%; Gap handling, STRIP). (A and B) The analysis included a sequence stretch of 1,500 bp from the start codon of the vif gene to the 5′ end of env, including vif, vpr, exon 1 of tat and rev, vpu, and the first 200 bp of env (A) and a ca. 700-bp fragment overlapping 300 bp from the 3′ end of env encompassing the complete nef gene and parts of the 3′ LTR (B). Positions of the start codons of vpr, tat, vpu, env, and nef, as well as the 5′ end of the 3′ LTR, are indicated by arrows above the diagrams. RIP analysis was based on background alignments using sequences derived from selected virus strains representing the most relevant HIV-1 subtypes. The indicated standard representatives are marked by different colors. The x axis indicates the nucleotide positions along the alignment. The y axis indicates the similarity of the 97cn54 to the listed reference subtypes. (C and D) RIP analysis of sequences from two independent clade C isolates (xj24 [C] and xj158 [D]) from China overlapping the vpr and vpu genes including the first exon of tat.