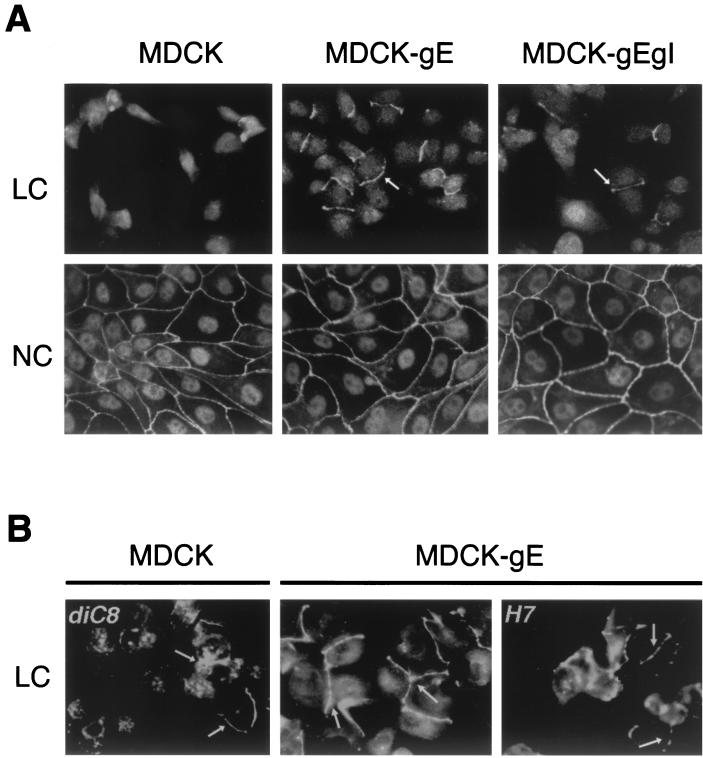
FIG. 3.
The effects of VZV gE on cell-cell adhesion and TJ formation. Clones of MDCK-gE and MDCK-gE/gI cells and MDCK controls were grown on glass coverslips in LC or NC medium for 20 h. Cells were fixed and permeabilized before incubation with rabbit anti-ZO-1 and FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG and were examined by confocal microscopy. (A) Membrane staining with ZO-1 is observed at cell contacts between MDCK-gE and MDCK-gE/gI cells but not between MDCK cells under LC conditions; MDCK cells under LC conditions have the characteristic morphology of single cells prior to triggering of monolayer formation by Ca2+. With the switch to NC medium, all cell lines have the expected localization of ZO-1 to cell-cell junctions. (B) diC8, a PKC agonist, permitted some localization of ZO-1 to cell membranes in MDCK cells under LC conditions, and ZO-1 localization in MDCK-gE-expressing cells became extensive; the PKC inhibitor H7 partially blocked TJ formation between MDCK-gE cells, resulting in a punctate pattern of ZO-1 under LC conditions. Arrows, ZO-1 protein.