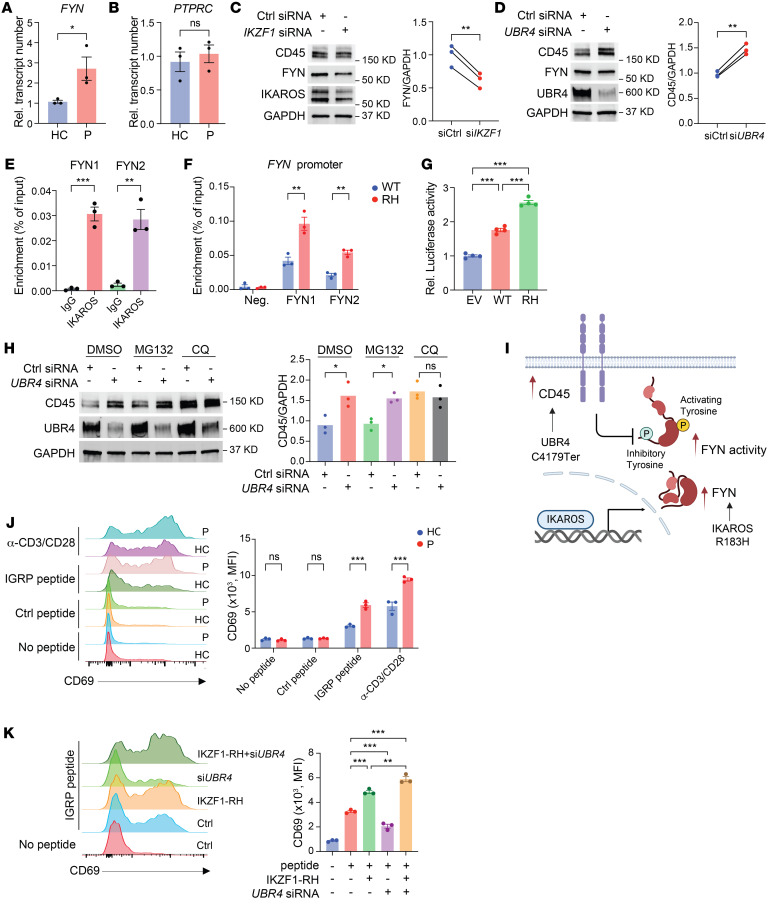
Figure 5. Synergistic function of IKAROS and UBR4 variants in causing FYN hyperactivity.
(A) FYN expression was determined by qPCR in T cell blasts derived from healthy controls (n = 3) and patients (n = 3). (B) PTPRC expression was determined by qPCR in T cell blasts derived from healthy controls (n = 3) and patients (n = 3). (C) Immunoblot analysis of total T cells from healthy individuals transfected with control (Ctrl) siRNA or IKZF1 siRNA. (D) Immunoblot analysis of total T cells from healthy individuals transfected with control siRNA or UBR4 siRNA. (E and F) ChIP-qPCR analysis of IKAROS binding with 2 FYN promoter primer sets. Total T cells derived from healthy controls were transduced with WT IKAROS (E) or with WT or the R183H IKFZ1 variant (F). (G) HEK293T cells were transfected with FYN promoter reporter constructs together with empty vector, vector encoding WT IKAROS, or the R183H variant (RH). Luciferase activity was determined 24 hours after transfection. (H) Immunoblot analysis of total T cells from healthy individuals transfected with control siRNA or UBR4 siRNA followed by DMSO, MG132 (10 μM), or CQ (50 μM) treatment for 8 hours. (I) Schematic representation of the synergistic function of IKAROS and UBR4. (J) T cells derived from healthy controls (n = 3) and patients (n = 3) were transduced with the T1D2 TCR transgene. Cells were stimulated with no peptide, control peptide, or IGRP peptide–loaded APCs and analyzed for the expression of CD69 by flow cytometry. Anti-CD3/anti-CD28 stimulation served as a positive control. (K) T1D2 TCR–transgenic T cells derived from a healthy control were transduced with the R183H IKZF1 variant or transfected with UBR4 siRNA. CD69 expression was determined after stimulation with no peptide or IGRP peptide–loaded APCs. Data represent the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, by 2-tailed, unpaired Student’s t test (A, B, E, and F), 2-tailed, paired Student’s t test (C and D), 1-way ANOVA (G, H, and K), or 2-way ANOVA (J).