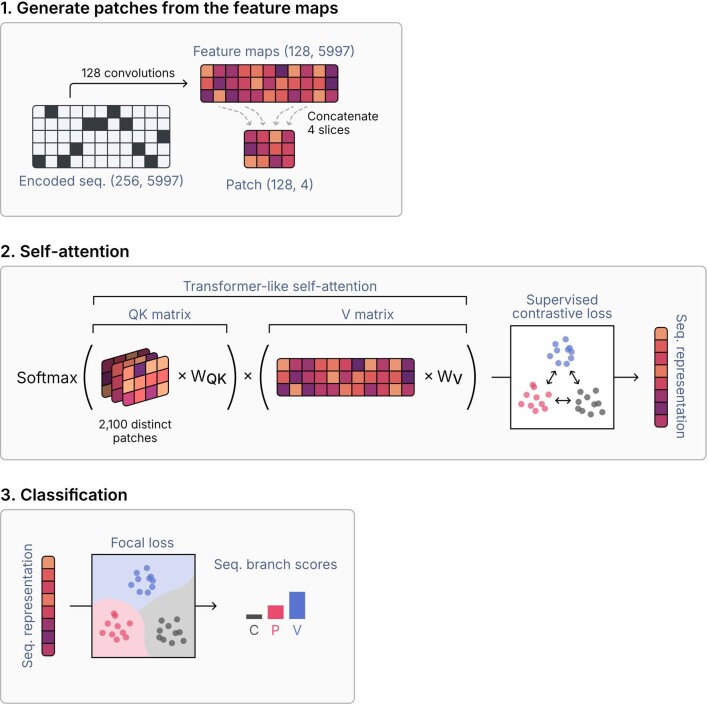
Extended Data Fig. 1. Global sequence representations generated by the IGLOO encoder are used for sequence classification.
(a) The IGLOO encoder applies 128 independent convolutions to the one-hot-encoded sequence to create a feature map, from which four random slices are taken and concatenated to generate patches that encode long-distance relationships within the sequence. (b) A total of 2,100 patches are used to weight different parts of the feature map in a transformer-like self-attention mechanism that results in a high-dimensional sequence representation. The encoder was trained using a supervised contrastive loss function, which optimizes the separation of the three classes (chromosome, plasmid, and virus) in the embedding space. (c) To classify sequences, the sequence representations generated by the IGLOO encoder are fed to a dense neural network trained with focal loss to account for class imbalance.