FIG. 4.
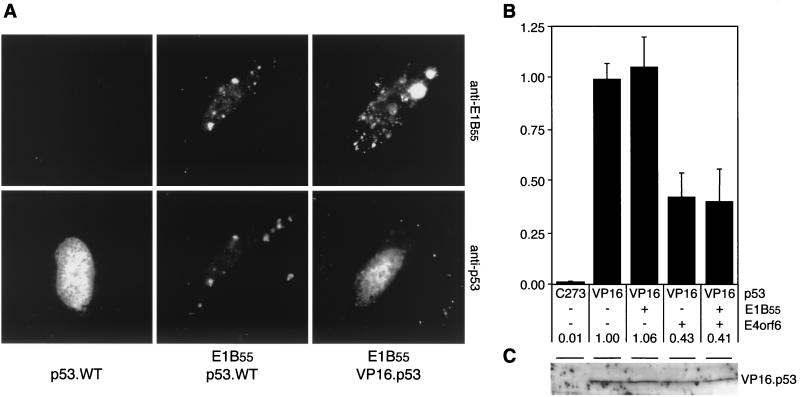
A functional interaction of E1B-55kDa with p53 is required for both transcriptional repression and downregulation of p53. (A) The chimeric VP16.p53 protein is not relocalized to perinuclear bodies by E1B-55kDa. Wild-type and chimeric p53 proteins were transiently expressed in Saos-2 cells in the absence or presence of E1B-55kDa, as indicated below the panels. The localization of E1B-55kDa and p53 proteins was determined by indirect immunofluorescence with antibody 2A6 (upper panel) and FL-393 (lower panel). Nuclear localization was confirmed by costaining cellular DNA with 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole (results not shown). (B) Transcriptional activity of VP16.p53 is repressed by E4orf6 but not by E1B-55kDa. Saos-2 cells were transfected with plasmids pPG13.Luc, pSV2.VP16.p53, pcDL.E1B55, pRK5.E4orf6.WT (at a ratio of 5:1:7.5), and pCMVβ. After 32 h, cells were harvested and processed as indicated in the legend to Fig. 3. Measured light units are indicated as relative activity compared to VP16.p53 alone. The numbers below the columns and error bars reflect the relative transactivation and the standard deviation of at least two experiments performed in duplicate. (C) Steady-state levels of transiently expressed VP16.p53 are not affected by E1B-55kDa and E4orf6. Saos-2 cells were transfected with expression plasmids for VP16.p53, E1B-55kDa, and E4orf6.WT (at a ratio of 3:3:4), as indicated on top. After 32 h, cells were harvested and lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with a polyclonal antibody to p53 (FL-393). In lane 1, a mock-transfected lysate of Saos-2 cells was applied. The position of VP16.p53 is indicated.