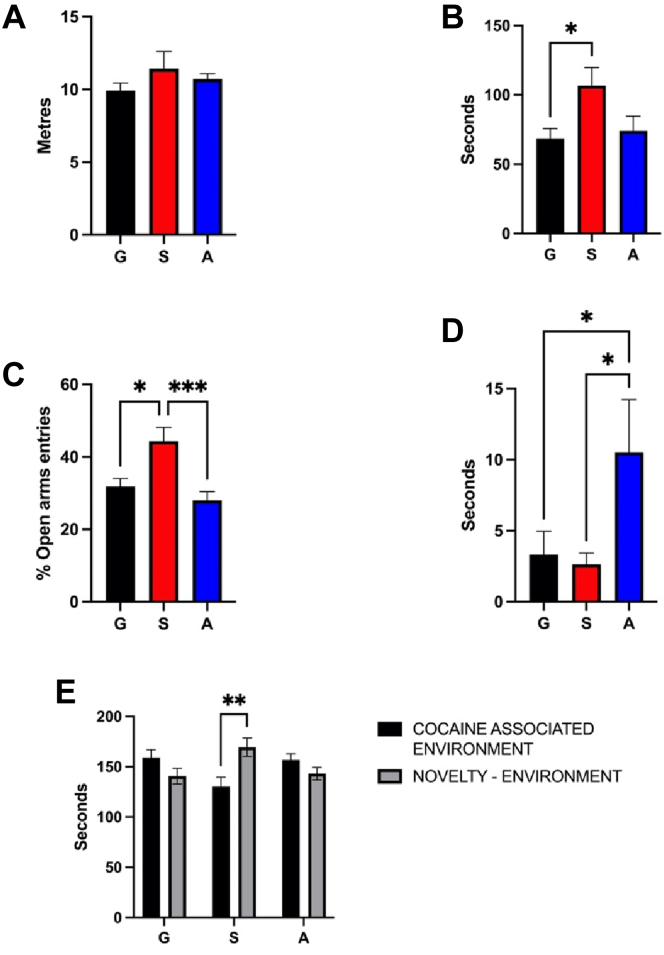
Fig. 6.
Effects of downregulating by shRNA (S), overexpressing (A) ARSB, and control group (G) in mice’s anxiety in the elevated plus maze and in mice’s preference for cocaine over novelty during cocaine withdrawal.A, the total activity of the control group (G), the shRNA ARSB group (S), and the upregulated ARSB group (A) during the test. B, one-way ANOVA revealed a significant difference between the groups in the time spent in the open arms. C, the percentage of entries in the open arms. D, the latency to the first entry in the open arms (F2,42 = 3.88, p < 0.05; F2,42 = 8.73, p < 0.001; F2,42 = 3.36, p < 0.05). Tukey post hoc revealed that S spent significantly more time in the open arms when compared to the control (G) (p < 0.05) and had a significantly higher percentage of entries in the open arms than G (p < 0.05) and A (p < 0.001). Moreover, Fisher post hoc revealed that A had a significantly higher latency to the first entry in the open arms than G (p < 0.05) and S (p < 0.05). In addition, two-way ANOVA revealed a significant effect of Group x Novelty interaction (F2,90 = 8.34, p < 0.001) in mice’s preference between cocaine and novelty. E, Tukey post hoc revealed that S significantly spent more time exploring the novelty (p < 0.01). ARSB, arylsulfatase B.