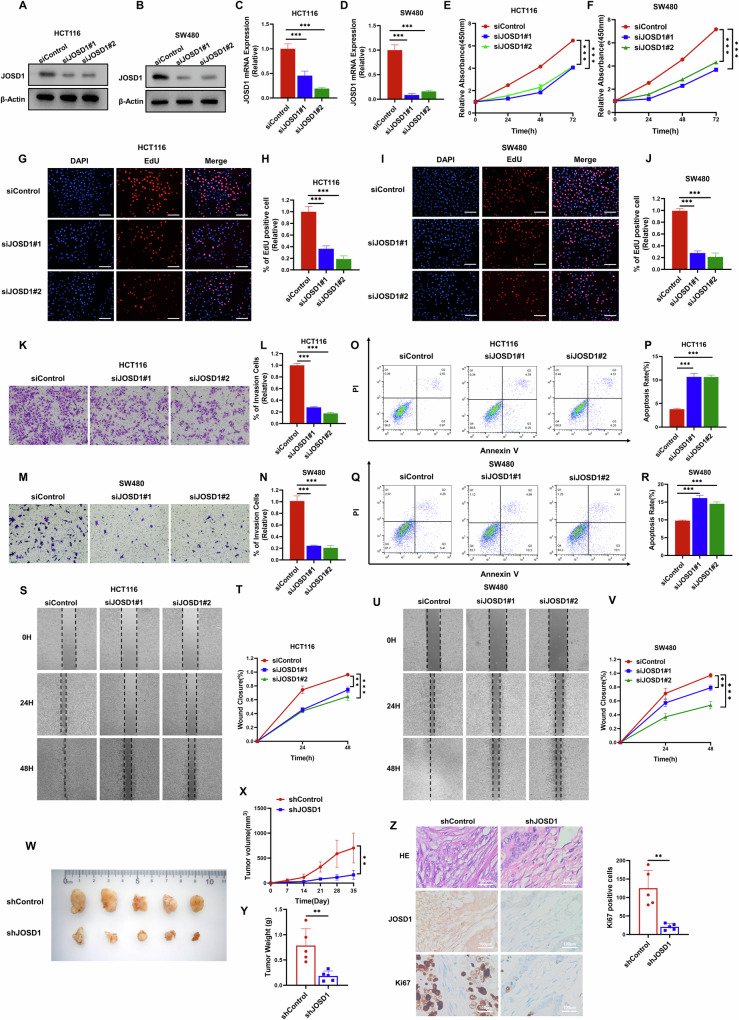
Fig. 2. JOSD1 is an important modulator for colon cancer cell progression.
A–D Immunoblot analysis and qRT–PCR were used to determine the expression level of JOSD1 in HCT116 and SW480 cells transfected with siControl or two independent siJOSD1. β-Actin was used as internal control. E, F The results showed that JOSD1 depletion inhibits the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells. Experiments were performed in triplicate. Statistical significance was observed for cell growth comparisons. G–J JOSD1 depletion resulted in a reduction in the number of EdU-positive colorectal cancer cells. K–N Depletion of endogenous JOSD1 significantly reduced cell invasion. O–R The depletion of JOSD1 promoted apoptosis in both HCT116 and SW480 cells. A quantitative summary of the apoptosis analysis was performed using FACS. S–V Depletion of JOSD1 inhibited the growth of colorectal tumors in vivo as demonstrated by the wound healing assay performed on HCT116 and SW480 cells with JOSD1 depletion or siControl transfection. W–Y The suppression of JOSD1 impacts xenograft tumor growth. Z The analysis of xenograft tumors revealed that depletion of JOSD1 led to reduced expression of Ki67, a marker of cell proliferation, in the tumors. The quantification of Ki67 positive cells showed a notable decrease in the right panel. All data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA.