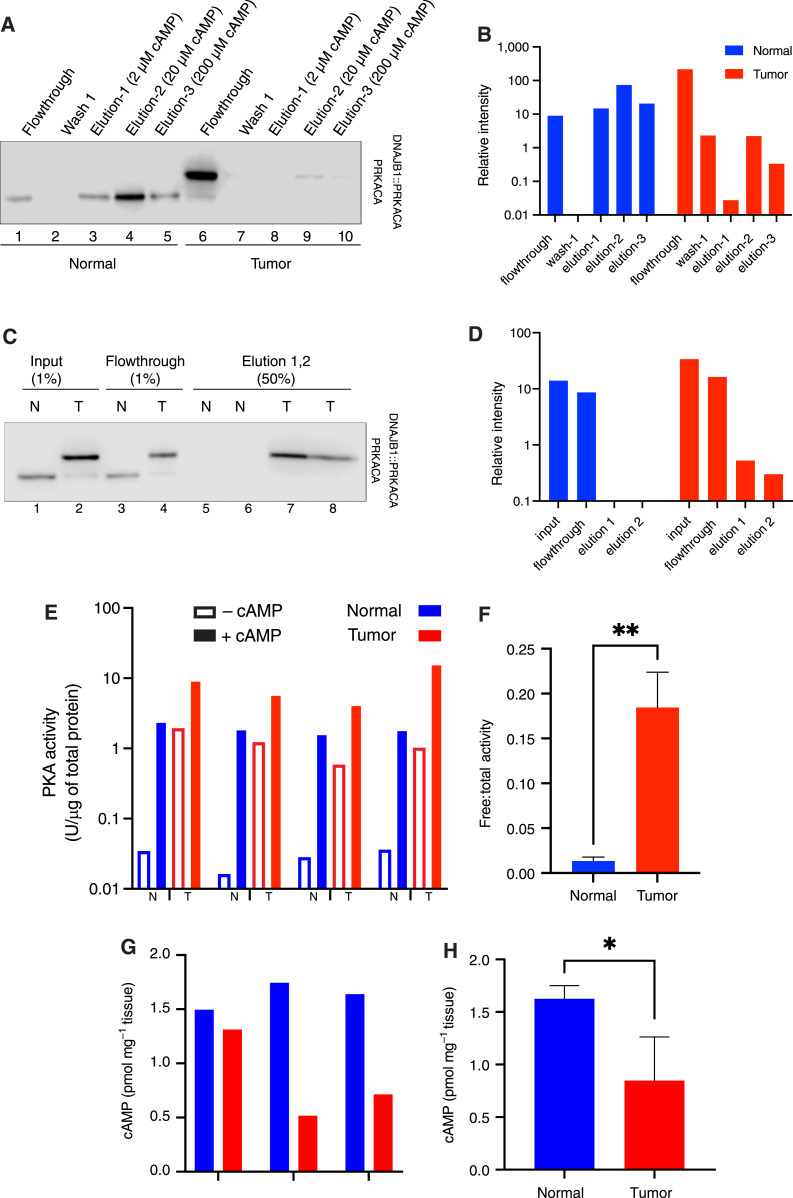
Figure 2.
Free PKA catalytic subunit and activity level in tumor vs. normal liver. A, DEAE-Sepharose resin pulldown. Human FLC normal and tumor liver lysate were incubated with DEAE resin. Unbound PKA C subunits (non-holoenzyme) flow through the column. Three washes were performed, followed by elution with increasing concentrations of cAMP. The flowthroughs, first wash, and elution were visualized by immunoblotting using an antibody to the carboxyl terminus of the C subunit, which recognizes both PRKACA (bottom band) and DNAJB1::PRKACA (top band). The same percent of each fraction was loaded on the gel. B, Quantification of PRKACA and DNAJB1::PRKACA bands from the Western blot in A. Blue, normal; red, tumor. C, GST-PKIα pulldown. Lysate from tumor and normal tissue was incubated with GST-PKI immobilized on glutathione Sepharose beads. Flowthrough was collected, and after three washes, catalytic subunits captured by GST-PKI were eluted with excess arginine. The percent of each fraction loaded on the gel is shown on the top of each well. D, Quantification of both PRKACA and DNAJB1::PRKACA from the Western blot on C. The loading percent in each well was counted for the quantification. Blue, normal; red, tumor. E, Free PKA (cAMP-independent, basal) activity is higher in tumor (T) tissue lysate than in normal (N) liver. FLC tumor has higher total PKA activity (in the presence of cAMP) than normal liver tissue. Results of paired tumor and normal tissue from four different patients. The first three are flash frozen and lysed by cryogrinding; the sample on the right is fresh and homogenized tissue. F, The ratio of free-to-total PKA (cAMP-dependent) in the flash-frozen tissue in tumor (red) compared to normal liver (blue). G and H, cAMP levels in tissue samples from three different patients (G) and the average of the three patients (H). t test was done using PRISM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005. Note the log scale in vertical axes of B, D, and E.