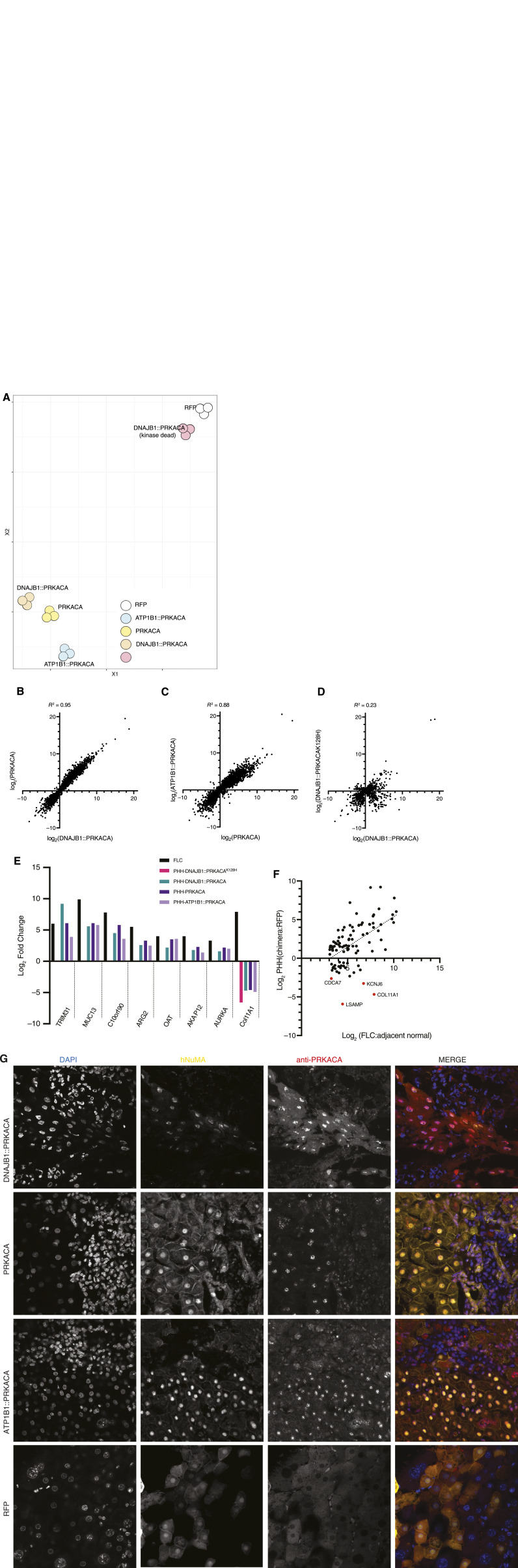
Figure 6.
Transcriptome in PHHs overexpressing PKA catalytic subunits. A, tSNE plot from whole transcriptomes of PHHs expressing PRKACA, DNAJB1::PRKACA, ATP1B1-PRKACA, DNAJB1::PRKACAK128H(inactive kinase), and RFP. B, Scatter plot comparing the |log2| fold change of the transcripts in PHHs expressing PRKACA (y-axis) to cells expressing DNAJB1::PRKACA (x-axis); transcripts = 7,406. C, Scatter plot comparing the |log2| fold change of the transcripts in PHHs expressing ATP1B1::PRKACA (y-axis) to cells expressing PRKACA (x-axis); transcripts = 7,986. D, Scatter plot comparing the |log2| fold change of the transcripts in PHHs expressing DNAJB1::PRKACAK128H (inactive kinase; y-axis) to cells expressing DNAJB1::PRKACA (x-axis); transcripts = 2,513; the number of transcripts are lower because there are fewer significant changes with the DNAJB1::PRKACAK128H. The R2 in B, C, and D was calculated by using the Pearson method using PRISM. E, Comparison of some of the known overexpressed transcripts in FLC with PHHs overexpressing DNAJB1::PRKACA, PRKACA, ATP1B1::PRKACA, and DNAJB1::PRKACAK128H. F, Scatter plot comparing the |log2| fold change of the transcripts in PHHs expressing DNAJB1::PRKACA with the |log2| fold change of the same transcripts in FLC for some of the most overexpressed transcripts in FLC tumors. G, Immunofluorescence on PHH implanted into mouse liver. The PHHs were transduced with top row, DNAJB1::PRKACA; second row, PRKACA; third row, ATP1B1::PRKACA; bottom row, RFP. All samples were probed with DAPI (left column); antibody to human nuclear mitotic apparatus (NuMA; second column); and antibody to the carboxyl terminus of PRKACA (third column). Merged image, fourth column. Each image is 210 μm by 210 μm.