Abstract
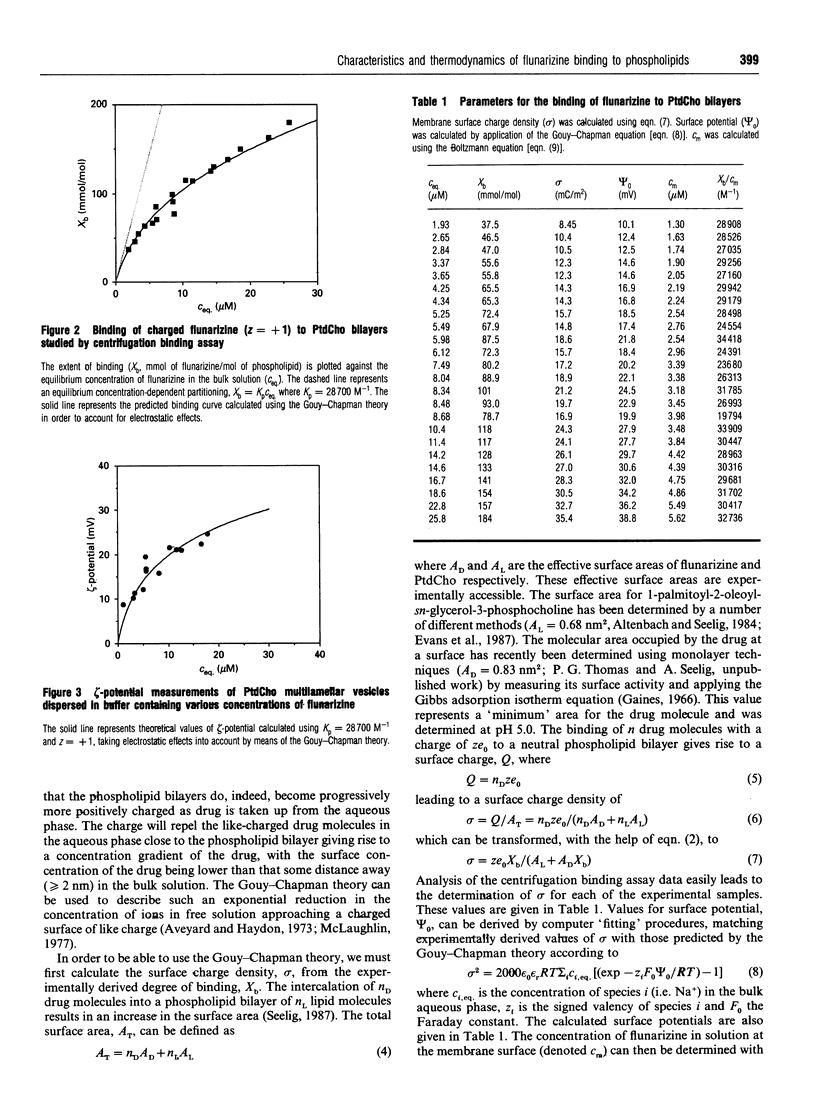
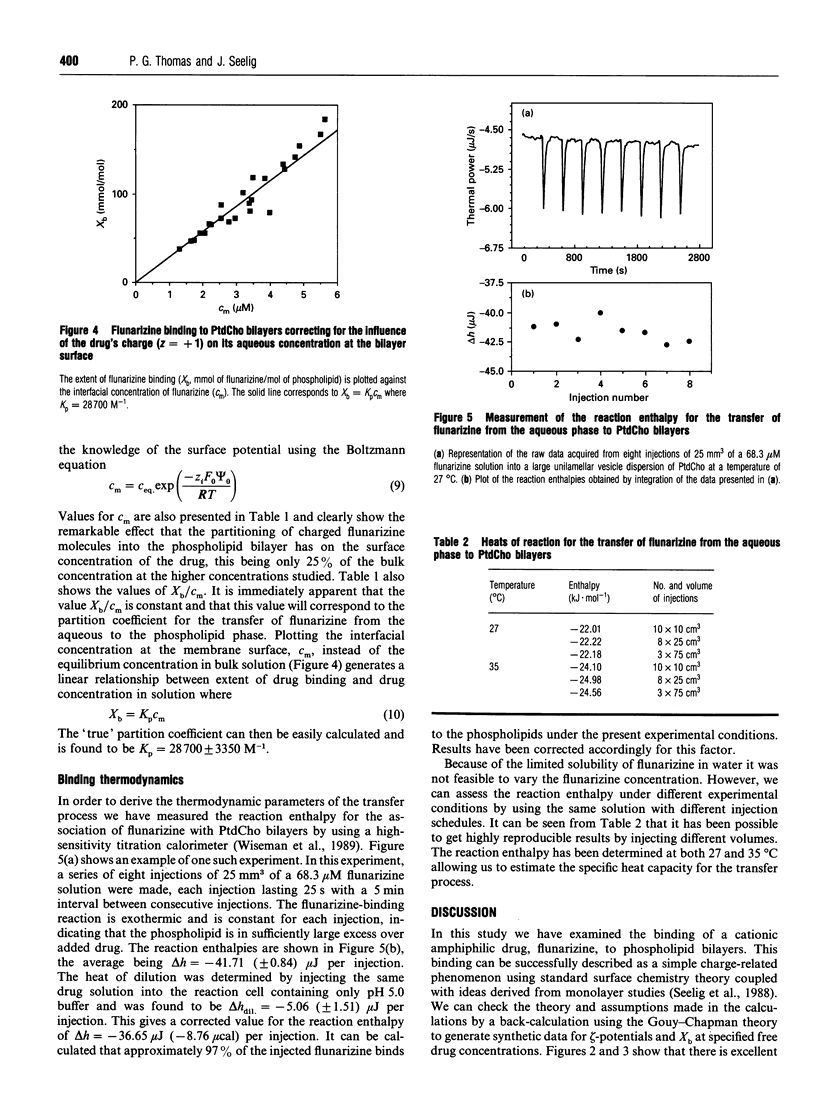
We have examined the partitioning/transfer of the Ca2+ antagonist flunarizine from the aqueous phase into phospholipid bilayers. We show that the binding of the cationic amphiphilic drug flunarizine to phospholipid bilayers displays traditional linear concentration-dependent characteristics once unmasked of electrostatic effects. The coefficient for the binding/partitioning of flunarizine to phosphatidylcholine was found to be 28700 M-1, supporting the notion that this drug may be particularly membrane-active. The thermodynamics of the partitioning/transfer process have also been studied using high-sensitivity titration calorimetry. Binding was found to be predominantly enthalpy-driven with only a small entropic contribution; delta H = -22.1 kJ.mol-1 (-5.3 kcal.mol-1) at 27 degrees C. This is in conflict with established ideas of entropy-driven partitioning of drugs into phospholipid membranes as a result of the 'hydrophobic effect'. The strong enthalpic nature of binding is interpreted as being indicative of strong lipophilic interactions between the drug and the phospholipid phase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenbach C., Seelig J. Ca2+ binding to phosphatidylcholine bilayers as studied by deuterium magnetic resonance. Evidence for the formation of a Ca2+ complex with two phospholipid molecules. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3913–3920. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäuerle H. D., Seelig J. Interaction of charged and uncharged calcium channel antagonists with phospholipid membranes. Binding equilibrium, binding enthalpy, and membrane location. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 23;30(29):7203–7211. doi: 10.1021/bi00243a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. W., Williams M. A., Tinoco J. Surface areas of 1-palmitoyl phosphatidylcholines and their interactions with cholesterol. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):455–462. doi: 10.1042/bj2450455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosey M. M., Lazdunski M. Calcium channels: molecular pharmacology, structure and regulation. J Membr Biol. 1988 Sep;104(2):81–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01870922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. H., Charlton J. P. Interactions of phosphatidylcholine vesicles with 2-p-toluidinylnaphthalene-6-sulfonate. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):735–740. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. The electrostatic properties of membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:113–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki J., Hideg K., Marsh D. Interfacial ionization and partitioning of membrane-bound local anesthetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jan 10;1103(1):62–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90057-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P. D., Subramanian S. Thermodynamics of protein association reactions: forces contributing to stability. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3096–3102. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Allegrini P. R., Seelig J. Partitioning of local anesthetics into membranes: surface charge effects monitored by the phospholipid head-group. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 7;939(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A. Local anesthetics and pressure: a comparison of dibucaine binding to lipid monolayers and bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 May 29;899(2):196–204. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Ganz P. Nonclassical hydrophobic effect in membrane binding equilibria. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9354–9359. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. G., Verkleij A. J. The dissimilar interactions of the calcium antagonist flunarizine with different phospholipid classes and molecular species: a differential scanning calorimetry study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Dec 14;1030(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd P. A., Benfield P. Flunarizine. A reappraisal of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in neurological disorders. Drugs. 1989 Oct;38(4):481–499. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198938040-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman T., Williston S., Brandts J. F., Lin L. N. Rapid measurement of binding constants and heats of binding using a new titration calorimeter. Anal Biochem. 1989 May 15;179(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


