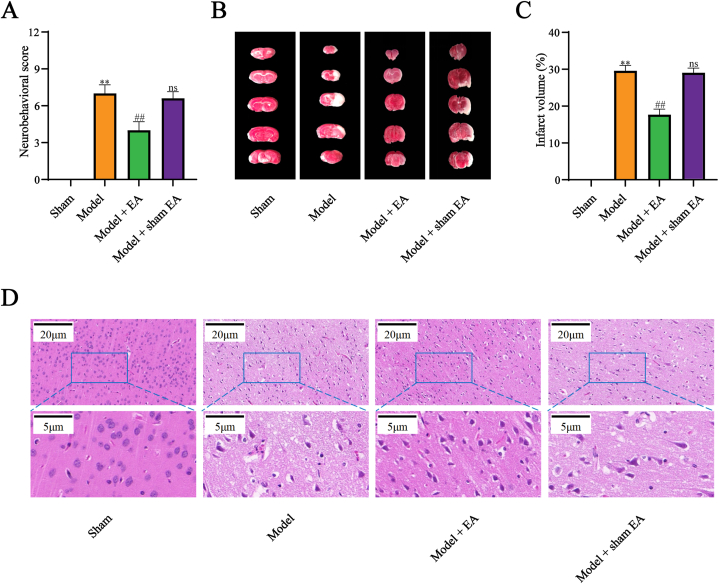
Fig. 2.
EA alleviated neurological deficits, infarct volume, and neuronal injury in cerebral I/R injury. (A) EA decreased neurobehavioral score in cerebral I/R injury (n=15). (B, C) EA reduced infarct volume in cerebral I/R injury (n=5). Red regions represented normal brain tissue while white regions represented infarcted brain tissue. (D) EA improved the pathological injury in cerebral I/R injury (n=5). All data are shown as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA followed by LSD post hoc test. ** indicates P < 0.01, compared with sham group; ns indicates not significant, ## indicates P < 0.01, compared with model group. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)