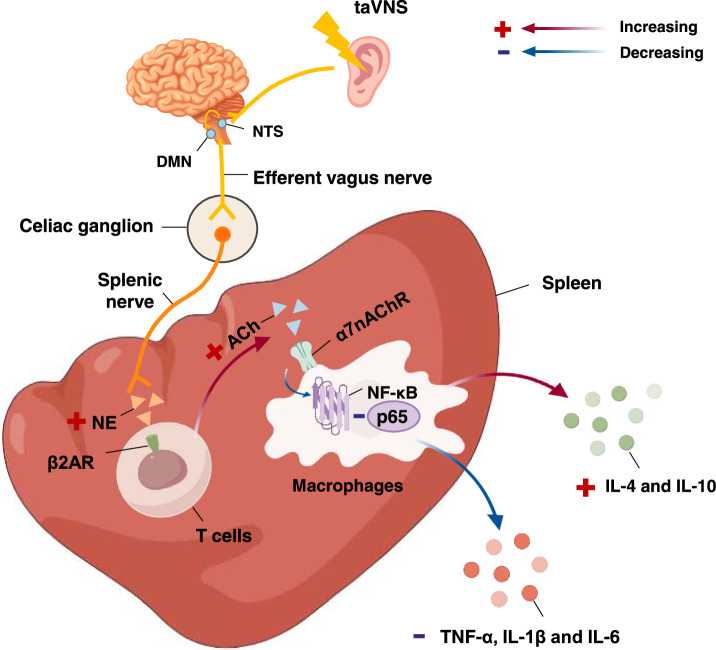
Figure 5.
Functional anatomy of taVNS in regulating immunity. After activation of NTS and DMN by taVNS, vagal efferent nerves modulate splanchnic nerves via the coeliac ganglion. The splanchnic nerve endings release norepinephrine, which prompts T cells to secrete acetylcholine, which then binds to α7nAChR on macrophages, inhibiting the NF-κB pathway and exerting anti-inflammatory effects. α7nAChR, nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 subunit; β2AR, β2-adrenergic receptor; ACh, acetylcholine; DMN, dorsal motor nucleus; IL, interleukin; NE, norepinephrine; NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB; NTS, nucleus tractus solitarius; taVNS, transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.