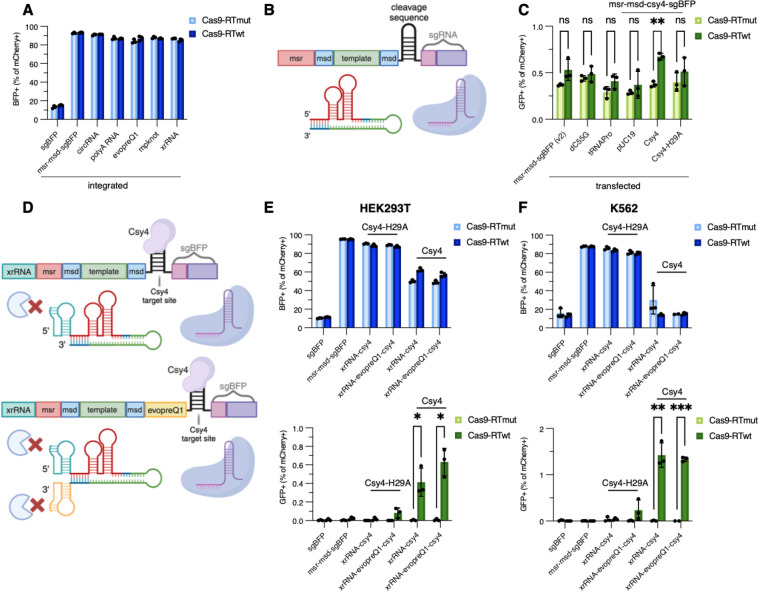
Figure 5. Optimization of post-transcriptional processing of ncRNAs to restore a native sgRNA 5’ end.
(A) BFP cutting efficiency of low-copy integrated structural ncRNAs. (B) Diagram of processed retron editor ncRNA. Either tRNA or Csy4 cleavage sequence allows separation of the retron template from sgRNA after transcription. (C) GFP editing efficiency of transfected processed retron editor ncRNAs. dC55G: mutated proline tRNA for improved processing, tRNAPro: full proline tRNA sequence, Csy4-H29A: nuclease deficient Csy4 mutant. (D) Diagram of pseudoknot protected and Csy4-protected retron editor ncRNAs. xrRNA-csy4 contains a single xrRNA pseudoknot on the 5’ end of the retron template, while xrRNA-evopreQ1-csy4 contains two pseudoknots that flank the retron template for both 5’ and 3’ protection after Csy4 processing. (E) Editing of BFP (top) and GFP (bottom) before and after ncRNA optimization in low-copy integrated HEK293T cells. (F) Same as Figure 5E done in low-copy integrated K562 cells. Error bars denote standard error of the mean.