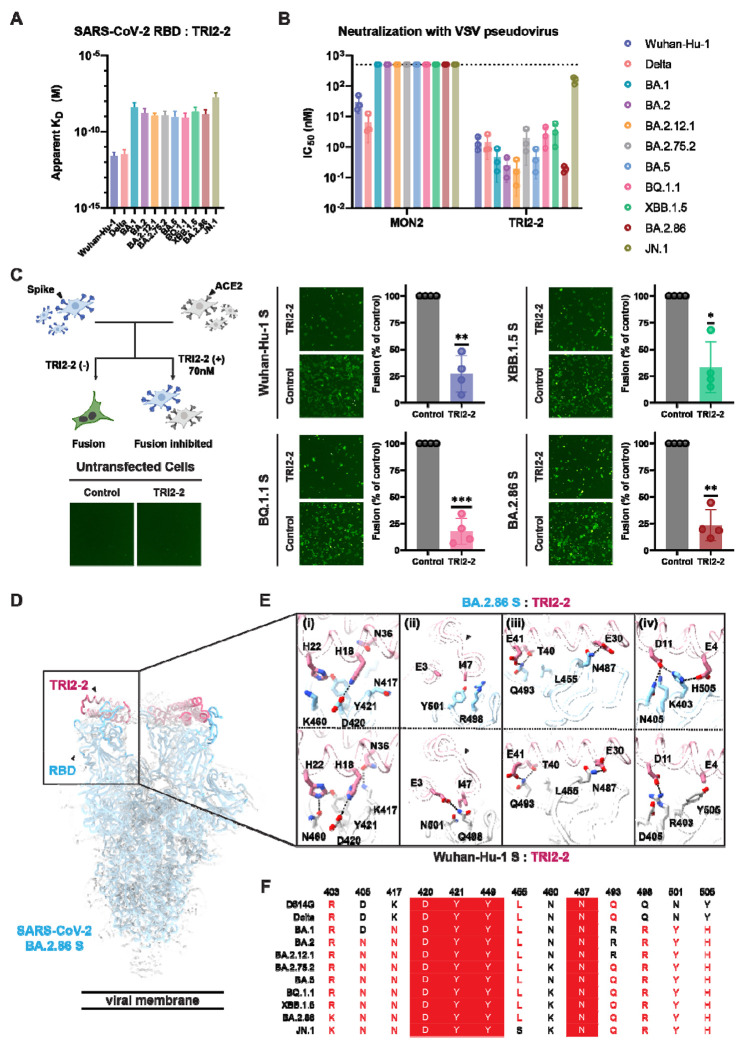
Figure 1. TRI2-2 cross-reacts with and potently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants.
(A) Binding of TRI2-2 to variant RBDs immobilized at the surface of BLI biosensors. Means of two biological replicates are shown as bar graphs with lines representing SD. (B) Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 S VSV pseudoviruses harboring the Wuhan-Hu-1 D614G, Delta, BA.1, BA.2, BA.2.12.1, BA.2.75.2, BA.5, BQ.1.1, XBB.1.5, BA.2.86, or JN.1 S. Means of three biological replicates (each replicate is shown as a circle) rendered as bar graphs with SD. (C) Cell-cell fusion assay between BHK21 cells expressing SARS-CoV-2 D614G, BQ.1.1, XBB.1.5, or BA.2.86 S glycoprotein and VeroE6-TMPRSS2 cells in the absence of TRI2-2 (control) or in the presence of 70nM TRI2-2. Each dot represents replicate from four different biological replicates. SDs shown as lines. One sample t tests between control and TRI2-2 treatment; ns, not significant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). The schematic of the cell-cell fusion assay was rendered using Biorender. (D-E) CryoEM structure of TRI2-2 bound to the BA.2.86 S glycoprotein trimer (electron potential map shown as a semi-transparent gray surface) (D) and close-up views of the binding interface between TRI2-2 and BA.2.86 RBD compared to that obtained in complex with the Wuhan-Hu-1 RBD (PDB 7UHB) (E). (F) Amino acid sequences of the key residues at the binding interface. Coloring scheme follows ESPript 318.