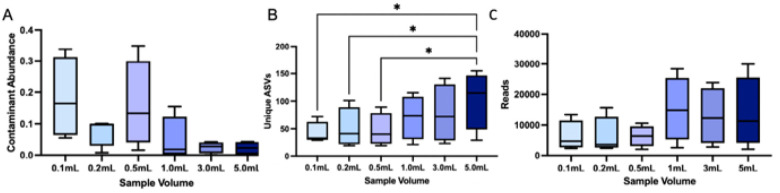
Figure 1. Urine sample volume influences contaminant abundance and microbial diversity (16S).
A) The abundance of contaminants (contaminating microbial sequences) decreased significantly as sample volume increased (overall p=0.026, Friedman, no pairwise comparisons were significant, Table S6). B) Microbial richness, or the number of unique amplicon sequence variants (ASVs), increased significantly with increased sample volume (p=0.015, Friedman) and 5.0mL samples had significantly greater numbers of unique ASVs compared to 0.5mL (p=0.031), 0.2mL (p=0.031), and 0.1mL samples (p=0.048), (multiple comparisons were FDR-corrected at 0.05, Table S7). C) Sequencing depth (reads) was increased at greater urine sample volumes although this difference was not significant (p=0.075, Friedman). Box and whisker plots show the median, IQR, and min/max.