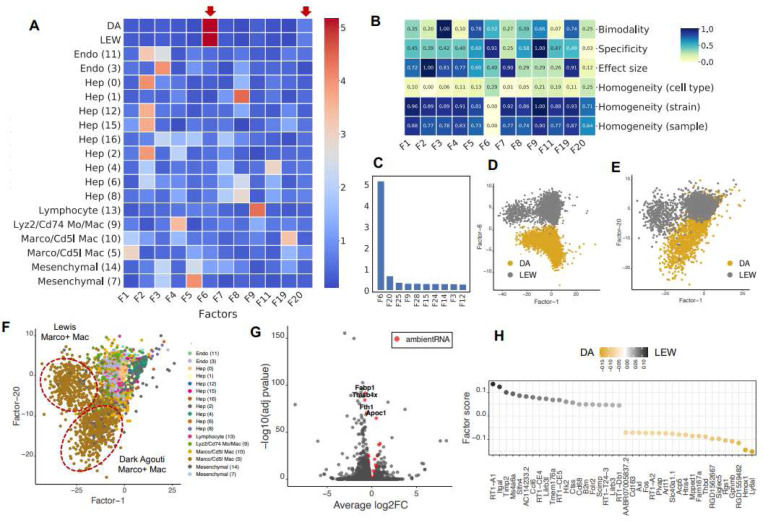
Figure 4). sciRED identifies strain-based variation despite ambient RNA contamination in a rat liver map.
We applied sciRED to a healthy atlas of the rat liver from two rat strains, Dark Agouti (DA) and Lewis (LEW) containing hepatocyte-derived ambient RNA contamination. A) FCA heatmap displaying covariate levels as rows and associated factors as columns. C) Factors F6 and F20 are most associated with strain variation. B) FIS heatmap illustrating the interpretability scores of the selected factors. D) Distribution of cells over factors F6 vs. F1 colored by strain and E) factors F20 vs. F1 colored by strain and F) by cell type, indicating that factor F20 captures strain variation within the myeloid population. G) Volcano plot of differential expression between strains within myeloid cells. Red dots are hepatocyte-derived ambient RNA transcripts as estimated by SoupX. Four hepatocyte genes—Fabp1, Tmsb4x, Fth1, and Apoc1—are labeled among the top differentially expressed genes within the myeloid cell type of both DA and LEW strains. These genes are among the top 50 ambient RNA transcripts derived from SoupX in all four rat liver samples (Table S2). H) Top 50 myeloid strain-associated genes identified by sciRED factor 20, free of contamination from hepatocyte-derived ambient RNA.