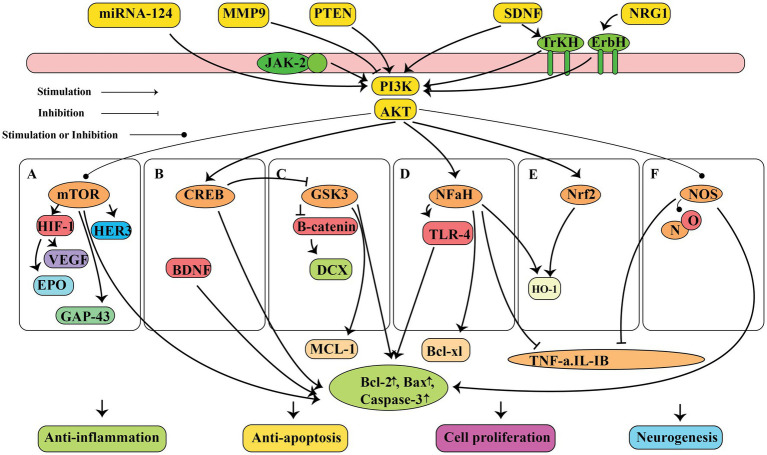
Figure 2.
The neuroprotective properties of ashwagandha is attributed to the molecular and pathway mechanisms, such as suppression of inflammation, inhibition of cell death, promotion of cell growth, and stimulation of neurogenesis. These effects are mediated by the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, which activates different pathways including mTOR, CREB, GSK3, NF-κB, Nrf2, and NOS. This figure adapted from Gu et al. (32).