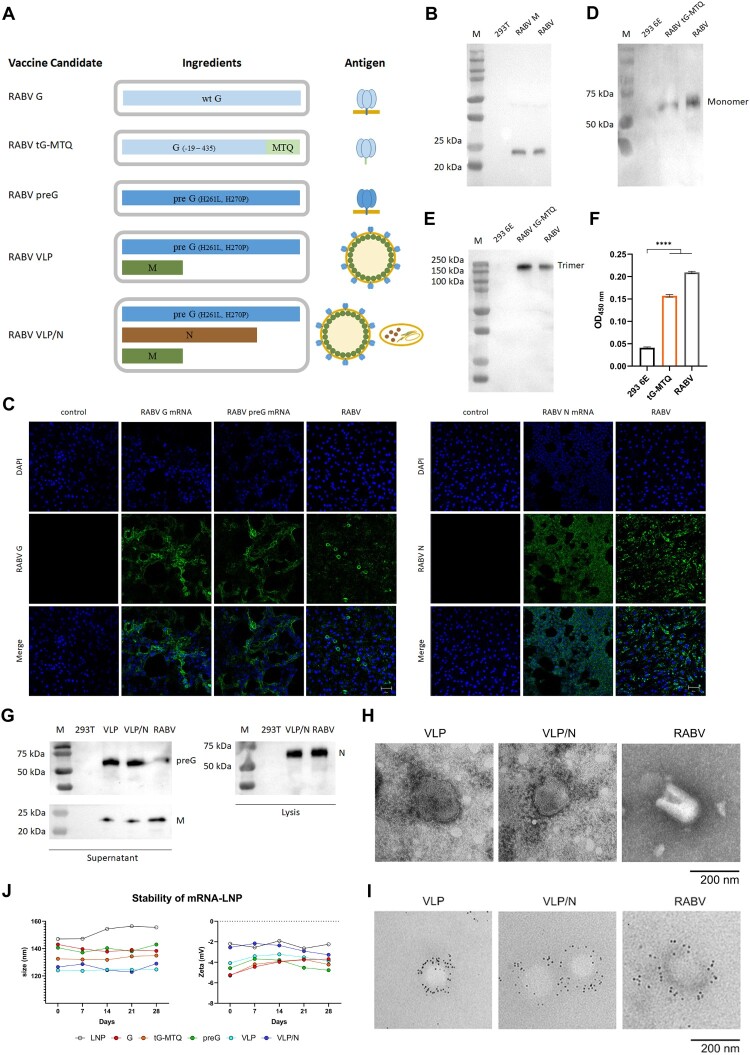
Figure 1.
Design and Characterization of RABV mRNA vaccines. (A) Schematic of five mRNA candidates for rabies. RABV G contains a mRNA encoding the full length of wild type RABV G. RABV tG-MTQ contains a mRNA encoding soluble truncated trimeric form of RABV G. RABV preG contains a mRNA encoding stabilized prefusion form of RABV G. RABV VLP contains two mRNAs encoding preG and M proteins that can self-assemble into VLPs. RABV VLP/N contains three mRNAs encoding preG, M, and N proteins. (B) Western blotting of RABV M protein. Expression of RABV M proteins were probed using mouse anti-RABV M polyclonal antibodies. (C) Immunofluorescence assays of the expression of RABV G, preG, and N proteins. 293 T cells were transfected with RABV G, preG, and N mRNA for 48 h, respectively, and detected by anti-rabies virus glycoprotein antibody and FITC-rabies virus nucleoprotein antibody. Scar bar: 50 μm. (D and E) Expression of the trimeric form of RABV G protein (tG-MTQ) was analyzed by SDS-PAGE, Native-PAGE, and western blottings, which showed that the monomeric and trimeric forms of tG-MTQ were approximately 57 and 150 kD, respectively. (F) Expression of the trimeric form of RABV G protein (tG-MTQ) was analyzed using a sandwich ELISA which were probed with mAbs 1112 and D1-25. (G) Western blotting assays of RABV VLPs. Expression of RABV preG, M or N proteins was probed using mouse anti-RABV G mAb, mouse anti-RABV M polyclonal antibodies and mouse anti-RABV N mAb. (H) Electron microscopy of VLPs. RABV VLP and VLP/N were concentrated by ultracentrifugation and prepared to negative staining for electron microscopy. Scar bar: 200 nm. (I) Immunoelectron microscopy of VLPs. RABV VLP and VLP/N were stained with mouse anti-RABV G mAb and then incubated with gold-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG antibody. Scar bar: 200 nm. (J) Stability of mRNA-LNPs stored at 4°C. Particle size and Zeta potential of six mRNA-LNPs detected in 28 d.