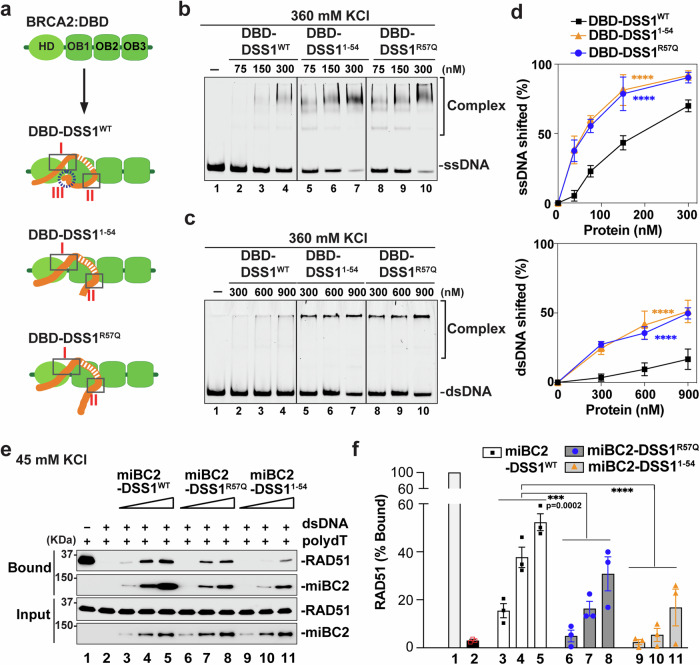
Fig. 3. Impact of DSS1 C-terminal Helix on DNA binding ability of DBD and targeting activity of miBRCA2-DSS1.
(See also Supplementary Figs. 8, 9). a Schematic representation of DBD-DSS1 complexes and their potential configurations. b Representative gel of ssDNA (5 nM) binding by DBD-DSS1WT, DBD-DSS11–54, and DBD-DSS1R57Q at 360 mM KCl condition. c Representative gel of dsDNA (5 nM) binding by DBD-DSS1WT, DBD-DSS11–54, and DBD-DSS1R57Q at 360 mM KCl condition. d Quantification (mean ± SD) of ssDNA (top) and dsDNA (bottom) binding from at least three independent experiments shown in b, c, ****p ≤ 0.0001 (two-way ANOVA). e Western blot analyses to monitor RAD51 loading by miBRCA2-DSS1WT (lanes 3–5; 3.75 nM, 7.5 nM, and 15 nM), miBRCA2-DSS1R57Q (lanes 6–8; 3.75 nM, 7.5 nM, and 15 nM), and miBRCA2-SS11–54 (lanes 9–11; 3.75 nM, 7.5 nM, and 15 nM) onto the ssDNA substrate at 45 mM KCl condition. Bead-biotin dT83 without dsDNA (lane 1) were served as a control. f Quantification of (e). The mean values (±SD) from three independent experiments were plotted, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001 (two-way ANOVA). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.