Fig. 3.
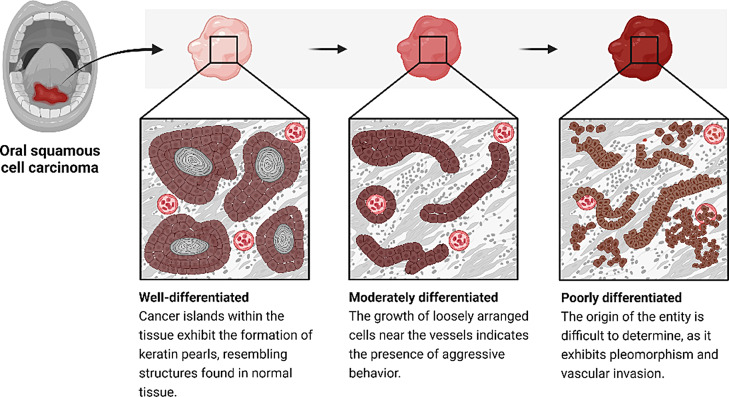
Histopathological examination of OSCC involves analyzing tissue sections from biopsied or surgically resected specimens. One of the key features evaluated is the differentiation of the tumor. Well-differentiated OSCC closely resembles normal squamous epithelium, exhibiting organized tissue architecture and possible keratinization. Moderately differentiated OSCC shows some loss of differentiation compared to normal cells, with variable sizes and shapes. Poorly differentiated OSCC bears little resemblance to normal squamous cells, lacking organized architecture and often appearing as sheets or cords of cells. Poorly differentiated OSCC tends to grow rapidly and has a higher likelihood of metastasis, resulting in a poorer prognosis compared to well-differentiated and moderately differentiated OSCC. Histopathological examination also considers other features such as tumor invasion patterns, nuclear characteristics, and the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate or desmoplastic reaction. Immunohistochemistry can provide additional information about differentiation, proliferation, and viral etiology, such as HPV infection. Overall, histopathology plays a critical role in diagnosing OSCC, determining its aggressiveness, and guiding treatment decisions