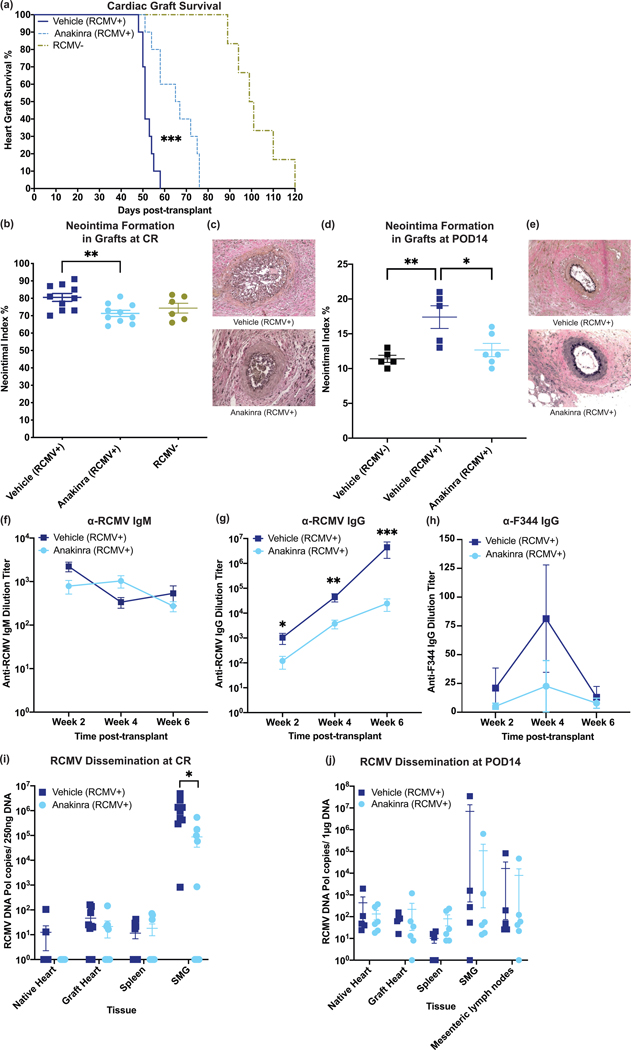
Figure 7.
One dose of anakinra at 1-hour post-transplant significantly improves survival time and decreases viral loads at rejection. Donor animals were infected with RCMV 5 days prior to transplantation. Recipients were then treated with vehicle or with anakinra at 1-hour post-transplantation. (a) Time to rejection was significantly improved by recipient treatment with anakinra following transplantation. Graft heart rejection was monitored by palpation for heart beat. Animals were sacrificed and tissues were harvested at the time of rejection. Vehicle treated animals had a mean survival time of 52 days and Anakinra treated animals had a mean survival time of 65 days. Statistical significance determined by Mann-Whitney test, ***P<0.001 vs. Vehicle-control, n=10. PBS-treated RCMV- historical controls included for references (light green) (b,c) Neointimal index of coronary arteries in graft hearts at chronic rejection was decreased in Anakinra-treated cohorts. Tissue sections were taken from graft hearts at the time of rejection and fixed in formalin. Tissue sections were stained with H&E and Elastin staining and the neointimal index was determined as an average of 6 coronary artery sections per animal (b). Representative images are shown in (c). Statistical significance was determined by Mann-Whitney test, **P<0.01, n=10. PBS-treated RCMV- historical controls included for references (light green). (d,e) Neointimal index of coronary arteries in graft hearts at POD14 was decreased in Anakinra-treated cohorts. Tissue sections were stained and the neointimal index was scored as in (b/c). Neointimal index scores are summarized in (d). Representative images are shown in (e). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction for multiple comparisons, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. n=6. (f-h) Anti-RCMV IgG antibody responses were reduced in Anakinra treated animals. Blood was taken from transplant recipients at 2, 4, and 6 weeks post-transplant until graft rejection. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays against anti-RCMV IgM (f) and IgG (g) antibodies and anti-F344 cardiac tissue IgG (h) antibodies were performed on serum samples and dilution titers were calculated for each sample. Averages for each cohort at 2, 4, and 6 weeks post-transplant are shown. n=10. Error bars represent SEM. Statistical significance determined by Mann-Whitney test, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. Vehicle-control. (i)Viral loads in tissues at rejection showed a significant decrease in the number of animals with detectable viral loads in SMG following Anakinra treatment. Tissues were harvested at time of cardiac graft rejection in RNAlater. Tissues were then homogenized in DNAzol and DNA was extracted. qPCR for RCMV viral DNA polymerase was used to quantitate RCMV genome copies in tissues. Error bars represent SEM. Statistical significance determined by fisher’s exact test, *p=0.0325 (two-tailed). (j) Viral loads in tissues at POD14 did not yet show significant impairment in viral loads in Anakinra-treated cohorts. Tissues were harvested as in (i). n=6.