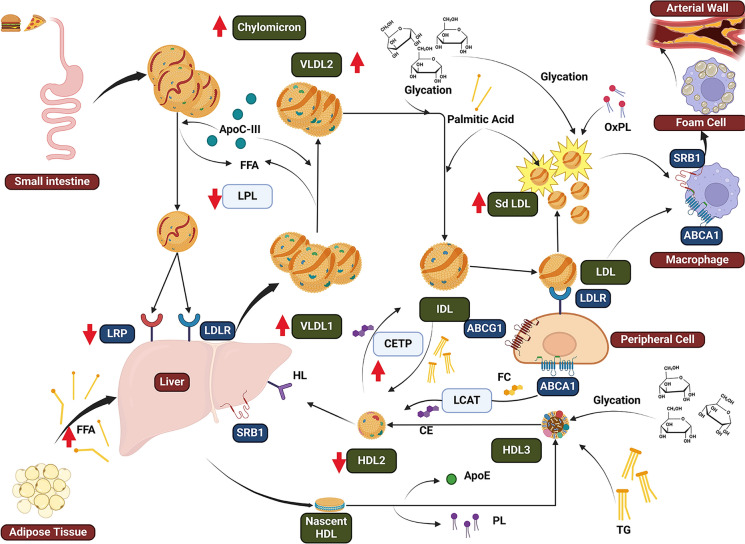
Fig. 1.
Overview of changes in type 2 diabetes dyslipidemia. Chylomicron in T2D there is an increased secretion of apoB-48, which is also stimulated by high circulating FFA. The delayed catabolism of chylomicrons is mainly due to metabolomic enrichment of apoC-III and reduced expression of LRP. VLDL overproduction, mainly VLDL1, produces an increased level of TG. There is both an increased production and delayed catabolism due to the increased FFA flux from adipocytes to liver. Metabolomic changes of VLDL include enrichment of apoC-III an inhibitor of LPL, which associated to glycation of apolipoproteins causes a reduced elimination. LDL has a reduced catabolism in T2D, inducing a longer half-life in plasma and promoting oxidation and production of sdLDL. As a consequence of hyperglycemia, there is glycation of LDL which further reduce the affinity to the receptors. HDL undergoes several changes in T2D as there is an increased activity of CETP and there is an enrichment of TG in HDLs. This promotes HL activity and results in an increased elimination of HDL from circulation. Also in T2D its known that HDL undergoes glycation and therefore has metabolomic changes (loss of phospholipid content and reduced apoE). apoB-100 apolipoprotein B-100, apoB-48 apolipoprotein B-48, apoC-III apolipoprotein C-III, apoE apolipoprotein E, CE cholesteryl ester, CETP cholesteryl ester transfer protein, CM chylomicron, FFAs free fatty acids, glycLDL glycated low-density lipoprotein, HL hepatic lipase, IDL intermediate density lipoprotein, LDLR low-density lipoprotein receptor, LPL lipoprotein lipase, sdLDL small, dense low-density lipoproteins, SR-B1 scavenger receptor B1, TG triglycerides, VLDL very-low-density lipoprotein