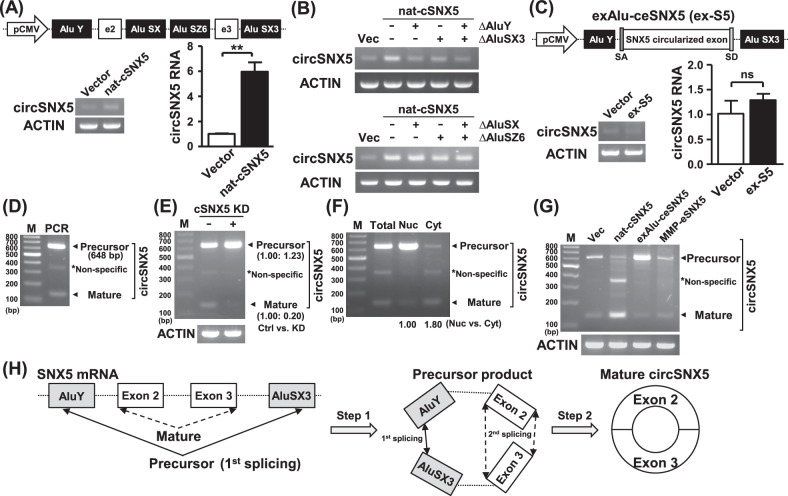
Fig. 3. CircSNX5 biogenesis operates by the sequential back-splicing mechanism.
A The circSNX5 vector (nat-cSNX5) was constructed and transfected into cells, and the expression efficiency was analyzed by end-point PCR and RT-qPCR assays. ACTIN expression served the loading control. B The mutant circSNX5 constructs were generated and delivered into cells, and the circSNX5 expression of transfectants was assessed by PCR assays. ACTIN expression served as internal control. C The circSNX5 construct (exAlu-ceSNX5) was transfected into cells, and the circSNX5 expression of transfectants was analyzed by end-point PCR and RT-qPCR analyses. ACTIN expression was used as the loading control. D PCR assays with increasing extension were performed, and the resulting products were visualized by gel electrophoresis. PCR amplicons were noted by the arrows while the asterisk (*) denotes non-specific signal. E CircSNX5 PCR analyses of indicated cells were performed, and ACTIN expression served the loading control. PCR products were analyzed by gel electrophoresis and further quantified. F CircSNX5 PCR assays of indicated samples were performed and analyzed by gel electrophoresis. PCR amplicons were noted by arrows and the asterisk. G CircSNX5 PCR analyses of transfectants were performed and analyzed by gel electrophoresis. ACTIN expression served the loading control. H Proposed model for the sequential back-splicing mechanism of circSNX5 biogenesis.