Fig. 1. Genome-wide analysis of the translatome is exploited to identify the extracellular interactome of prostate cancer - PMN-MDSCs.
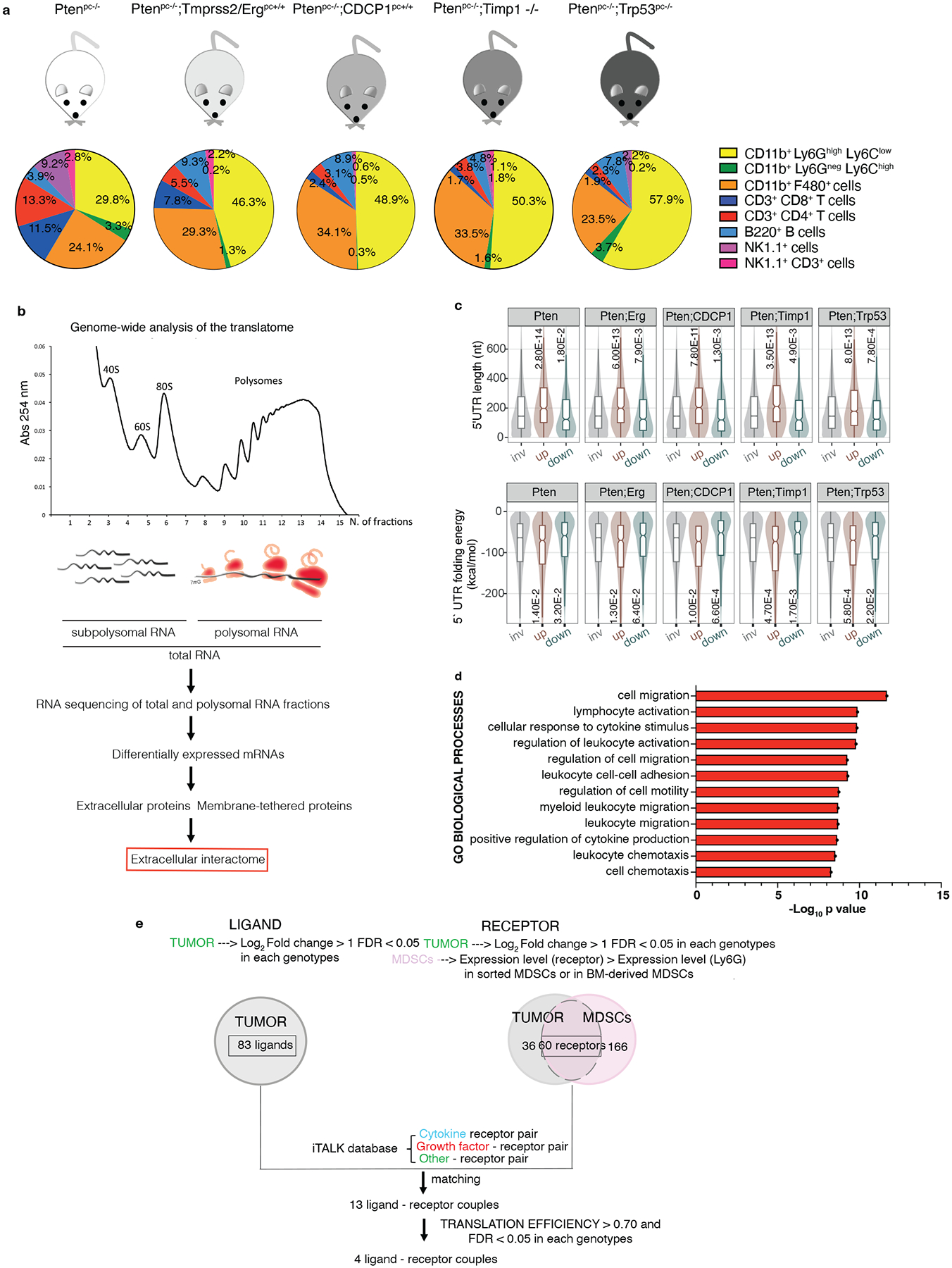
a, Immunophenotype of Ptenpc−/− (n = 4), Ptenpc−/−;TMPRSS2/Erg pc+/+ (at least n = 3), Ptenpc−/−;CDCP1pc+/+ (at least n = 2), Ptenpc−/−;Timp1−/− (n = 3) and Ptenpc−/−;Trp53pc−/− (n = 5) prostate cancers. b, Scheme of the polysome profiling analysis. c, Features of the 5’ UTRs of the translationally regulated mRNAs: 5’ UTR estimated length (top) and folding energy comparison (bottom). The mRNAs with an increased translation efficiency (TE) and the mRNAs with a decreased TE (down) were compared to mRNAs with a not significantly changed TE (inv) for each indicated genetic background (n = 3 mice) compared to wild-ty prostates (n = 3 mice). Definition of box whisker plots: center: median of the distribution; box: between lower and upper quartile; whisker: 1.5 interquartile range; outliers not displayed. Statistical test: Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test (two-sided). d, Gene Ontology Biological processes enriched among the translationally upregulated mRNAs in Ptenpc−/−, Ptenpc−/−;TMPRSS2/Ergpc+/+; Ptenpc−/−;CDCP1pc+/+, Ptenpc−/−;Timp1−/− and Ptenpc−/−;Trp53pc−/− prostate cancer compared to wild-type prostate, determined by the DAVID software. (n = 3 mice for each genetic background for a total of 18 samples). Log10 adjusted p-values by using the linear step-up method of Benjamini are reported. e, Bioinformatic algorithm applied to identify the extracellular interactome of prostate cancer - PMN-MDSCs.
