Figure. Age-adjusted percentage of patients with concurrent opioid and benzodiazepine prescriptions in 2016 and relative reduction in the percentage in 2019 versus 2016 by state.
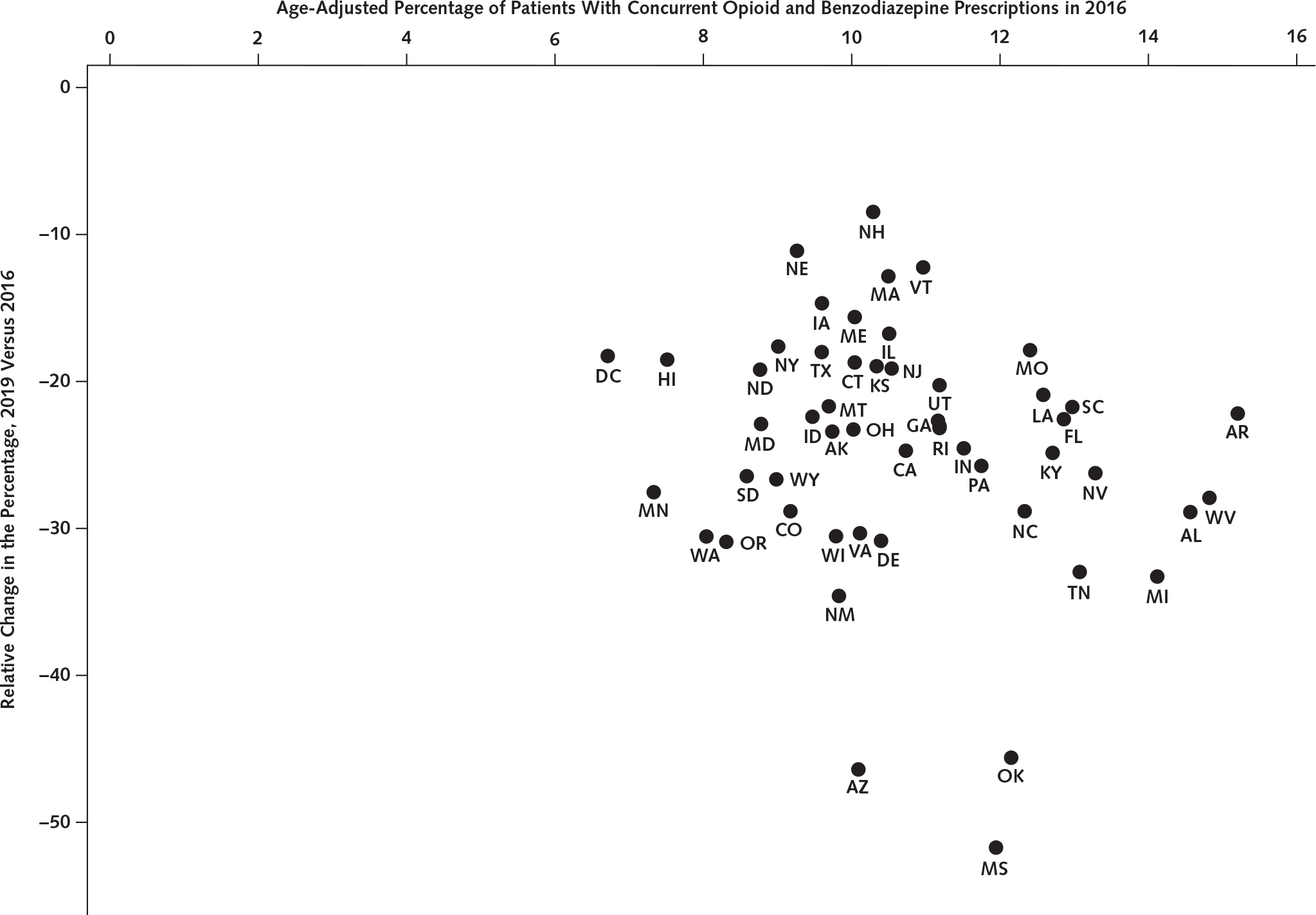
Source: Our analysis of the IQVIA Longitudinal Prescription (LRx) database 2016 to 2019. Geographic location of prescriptions was based on prescriber practice location (state). The percentage of patients with concurrent prescriptions for each state was estimated as annual total patients with concurrent prescriptions divided by annual total patients receiving an opioid in the state. The age adjustment was done based on the age group distribution of the denominator (number of patients receiving an opioid) for each state. AK = Alaska; AL = Alabama; AR = Arkansas; AZ = Arizona; CA = California; CO = Colorado; CT = Connecticut; DC = District of Columbia; DE = Delaware; FL = Florida; GA = Georgia; HI = Hawai’i; IA = Iowa; ID = Idaho; IL = Illinois; IN = Indiana; KS = Kansas; KY = Kentucky; LA = Louisiana; MA = Massachusetts; MD = Maryland; ME = Maine; MI = Michigan; MN = Minnesota; MO = Missouri; MS = Mississippi; MT = Montana; NC = North Carolina; ND = North Dakota; NE = Nebraska; NH = New Hampshire; NJ = New Jersey; NM = New Mexico; NV = Nevada; NY = New York; OH = Ohio; OK = Oklahoma; OR = Oregon; PA = Pennsylvania; RI = Rhode Island; SC = South Carolina; SD = South Dakota; TN = Tennessee; TX = Texas; UT = Utah; VA = Virginia; VT = Vermont; WA = Washington; WI = Wisconsin; WV = West Virginia; WY = Wyoming.
