Abstract
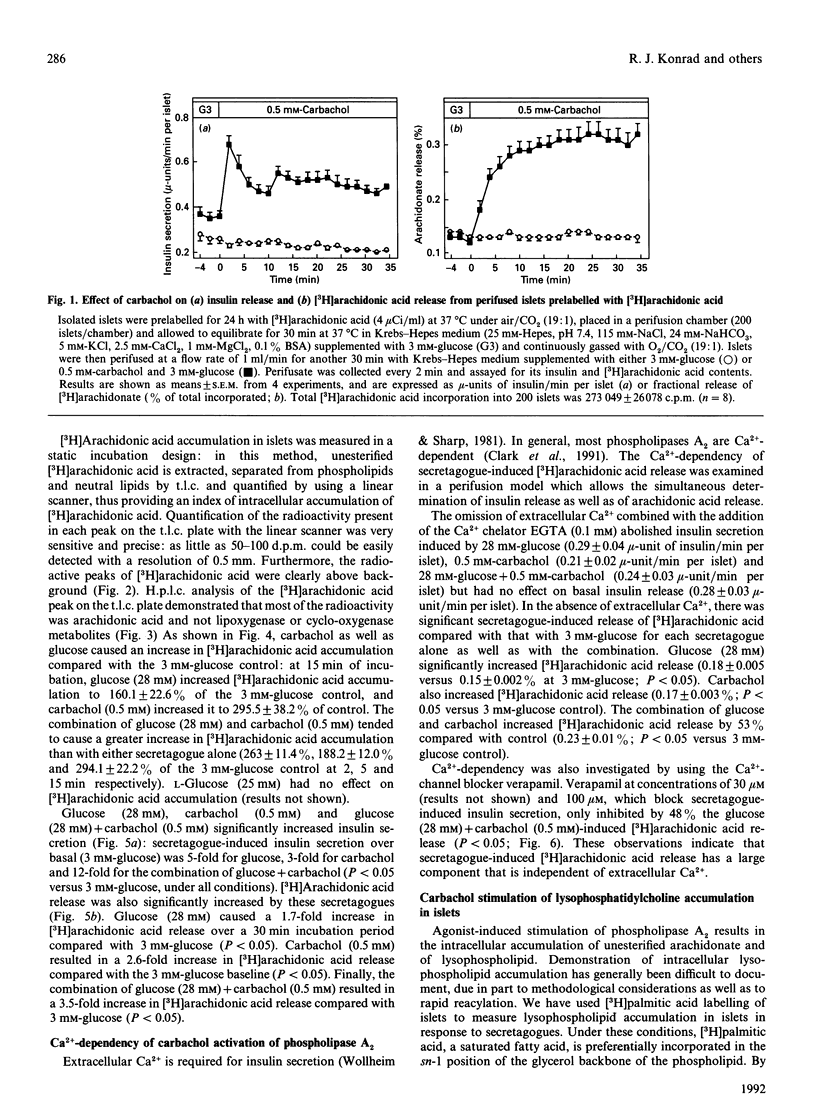
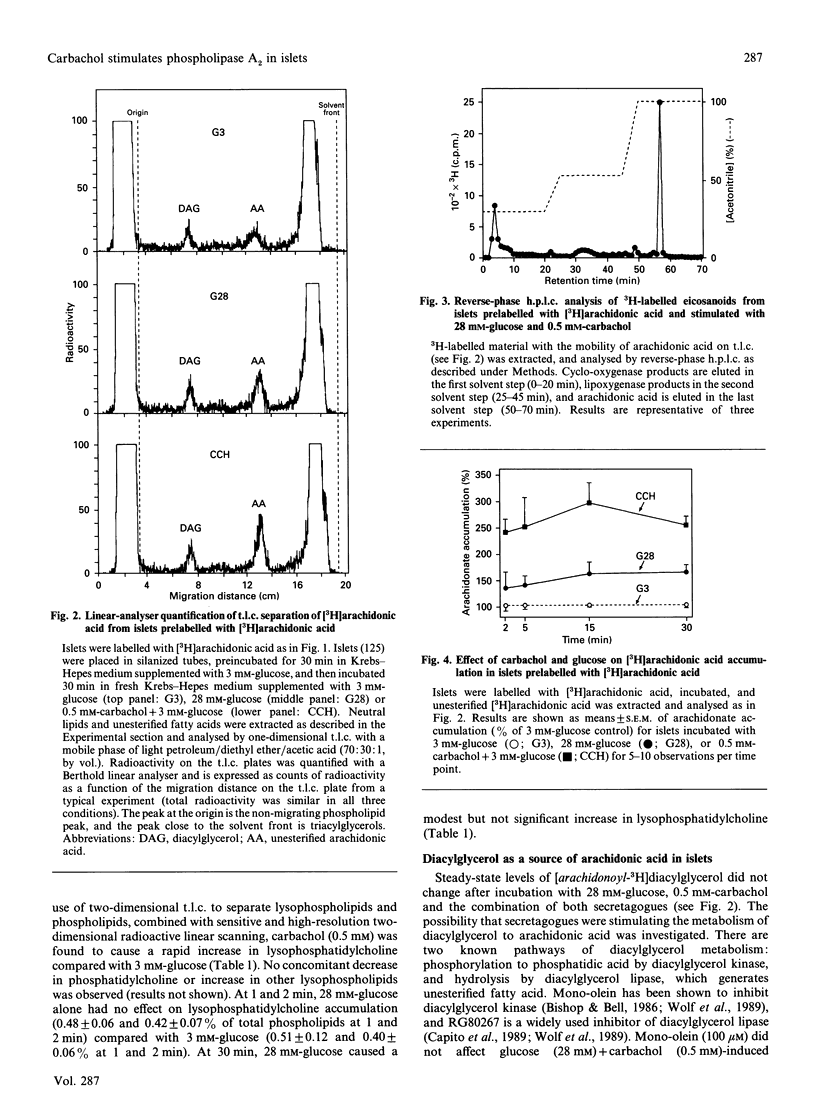
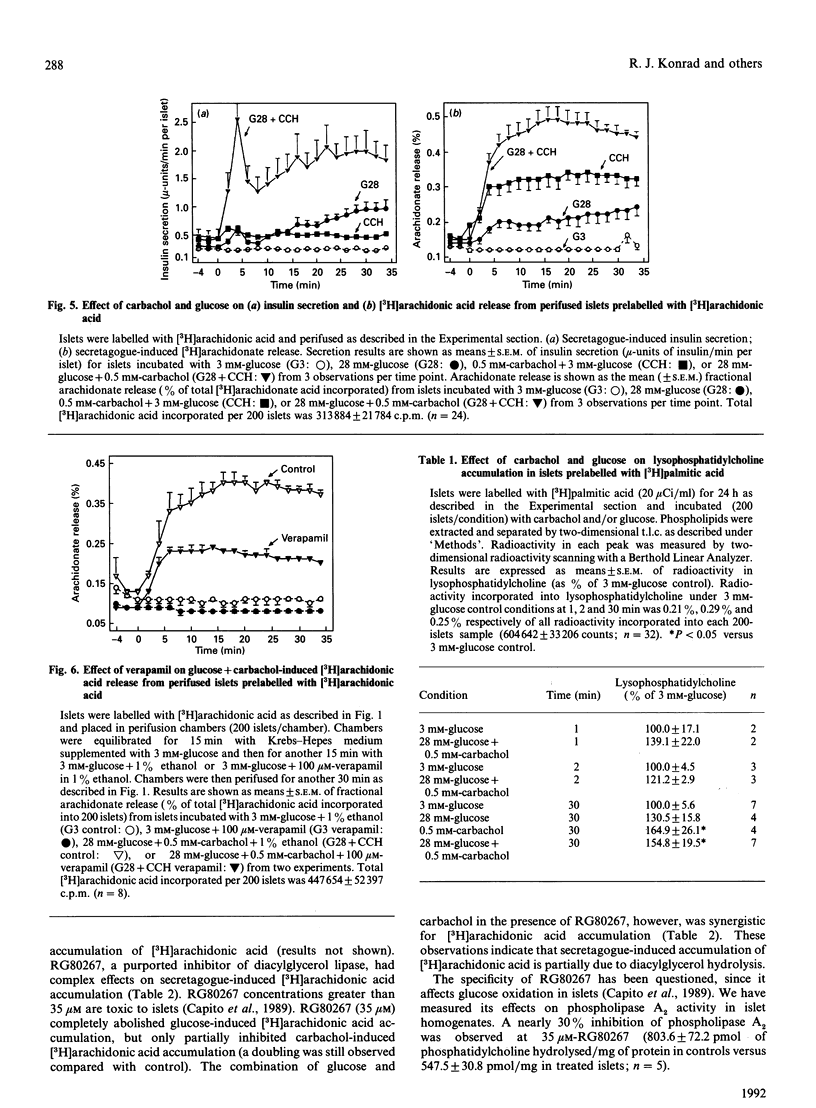
Arachidonic acid has been implicated as a second messenger in insulin secretion by islets of Langerhans. D-Glucose, the major physiological stimulus, increases unesterified arachidonate accumulation in islets. We now show, for the first time, that the muscarinic agonist carbachol, at concentrations which stimulate insulin secretion, causes a rapid and nearly 3-fold increase in arachidonic acid accumulation in islets. The combination of glucose and carbachol has an additive effect on unesterified arachidonate release. There is a large component of secretagogue-induced arachidonate accumulation that is independent of extracellular Ca2+. Carbachol stimulation of arachidonic acid release is mediated by activation of phospholipase A2, as demonstrated by early increases in endogenous lysophosphatidylcholine. In addition to phospholipase A2 activation, carbachol-induced arachidonic acid accumulation also appears to involve diacylglycerol hydrolysis, since the diacylglycerol lipase inhibitor RG80267 partly inhibited arachidonic acid accumulation. In contrast, glucose-induced arachidonic acid accumulation appears to reflect diacylglycerol hydrolysis entirely. Our observations indicate that phospholipase A2 has an important role in muscarinic-induced insulin secretion.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft S. J. Glucoreceptor mechanisms and the control of insulin release and biosynthesis. Diabetologia. 1980 Jan;18(1):5–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01228295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badiani K., Arthur G. 2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine lysophospholipase A2 activity in guinea-pig heart microsomes. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 15;275(Pt 2):393–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2750393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Peter-Riesch B., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B. Ca2+-mediated generation of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate and inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in pancreatic islets. Studies with K+, glucose, and carbamylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3567–3571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop W. R., Bell R. M. Attenuation of sn-1,2-diacylglycerol second messengers. Metabolism of exogenous diacylglycerols by human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12513–12519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buday L., Faragó A. Dual effect of arachidonic acid on protein kinase C isoenzymes isolated from rabbit thymus cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80547-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capito K., Hansen S. E., Hedeskov C. J., Thams P. Effect of diacylglycerol lipase inhibitor RHC 80267 on pancreatic mouse islet metabolism and insulin secretion. Diabetologia. 1989 Feb;32(2):111–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00505183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. M., Turk J. Mechanism of arachidonic acid-induced Ca2+ mobilization from rat liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 22;928(2):186–193. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Lin L. L., Kriz R. W., Ramesha C. S., Sultzman L. A., Lin A. Y., Milona N., Knopf J. L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90556-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colca J. R., Wolf B. A., Comens P. G., McDaniel M. L. Protein phosphorylation in permeabilized pancreatic islet cells. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):529–536. doi: 10.1042/bj2280529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Satin L. S., Ashford M. L., Hales C. N. ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pancreatic beta-cells. Spare-channel hypothesis. Diabetes. 1988 May;37(5):495–498. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.5.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. E., Larkins R. G. Activity of endogenous phospholipase C and phospholipase A2 in glucose stimulated pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):820–827. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. E., Larkins R. G. Muscarinic-agonist and guanine nucleotide activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in isolated islet-cell membranes. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):731–737. doi: 10.1042/bj2400731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M., Metz S. A. A phospholipase D-like mechanism in pancreatic islet cells: stimulation by calcium ionophore, phorbol ester and sodium fluoride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 15;163(2):922–928. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92310-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. Potassium selective ion channels in insulin-secreting cells: physiology, pharmacology and their role in stimulus-secretion coupling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 7;1071(1):67–82. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90012-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easom R. A., Landt M., Colca J. R., Hughes J. H., Turk J., McDaniel M. Effects of insulin secretagogues on protein kinase C-catalyzed phosphorylation of an endogenous substrate in isolated pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14938–14946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto W. Y., Metz S. A. Phasic effects of glucose, phospholipase A2, and lysophospholipids on insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1987 May;120(5):1750–1757. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-5-1750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto W. Y., Teague J. Phasic effects of glucose, p-hydroxymercuribenzoate, and lysophosphatidylcholine on insulin secretion from HIT cells. Diabetes. 1989 May;38(5):625–628. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.5.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan S., Calle R., Zawalich K., Smallwood J. I., Zawalich W. S., Rasmussen H. Glucose-induced translocation of protein kinase C in rat pancreatic islets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9893–9897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. C., Hermans M. P., Henquin J. C. Glucose-, calcium- and concentration-dependence of acetylcholine stimulation of insulin release and ionic fluxes in mouse islets. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 15;254(1):211–218. doi: 10.1042/bj2540211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A., Ronner P., Cheong E., Khalid P., Matschinsky F. M. The role of ATP and free ADP in metabolic coupling during fuel-stimulated insulin release from islet beta-cells in the isolated perfused rat pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):22887–22892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen S. L., Loeb L. A., Gross R. W. Purification and characterization of cytosolic phospholipase A2 activities from canine myocardium and sheep platelets. Methods Enzymol. 1991;197:400–411. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)97166-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedeskov C. J. Mechanism of glucose-induced insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1980 Apr;60(2):442–509. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.2.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Nenquin M. The muscarinic receptor subtype in mouse pancreatic B-cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 15;236(1):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Williams R. J., Corkey B. E., Matschinsky F. M., Williamson J. R. The effect of inositol trisphosphate on Ca2+ fluxes in insulin-secreting tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):12952–12955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrad R. J., Jolly Y. C., Wolf B. A. Glucose and carbachol synergistically stimulate phosphatidic acid accumulation in pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 31;180(2):960–966. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Walker M. M., Fink C. J. Perifusion of isolated rat islets in vitro. Participation of the microtubular system in the biphasic release of insulin. Diabetes. 1972 Oct;21(10):987–998. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.10.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laychock S. G. Coordinate interactions of cyclic nucleotide and phospholipid metabolizing pathways in calcium-dependent cellular processes. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1989;30:203–242. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152830-0.50009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laychock S. G. Fatty acids and cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase pathway inhibitors modulate inositol phosphate formation in pancreatic islets. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;37(6):928–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laychock S. G. Phospholipase A2 activity in pancreatic islets is calcium-dependent and stimulated by glucose. Cell Calcium. 1982 Mar;3(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. J. Elusive proximal signals of beta-cells for insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1990 Dec;39(12):1461–1466. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.12.1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Herchuelz A., Hutton J. C. Insulin release: the fuel hypothesis. Metabolism. 1979 Apr;28(4):373–386. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschinsky F. M. Glucokinase as glucose sensor and metabolic signal generator in pancreatic beta-cells and hepatocytes. Diabetes. 1990 Jun;39(6):647–652. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.6.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel M. L., Colca J. R., Kotagal N., Lacy P. E. A subcellular fractionation approach for studying insulin release mechanisms and calcium metabolism in islets of Langerhans. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:182–200. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meglasson M. D., Matschinsky F. M. Pancreatic islet glucose metabolism and regulation of insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1986;2(3-4):163–214. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610020301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Arachidonic acid and its metabolites: evolving roles as transmembrane signals for insulin release. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1988;32(3):187–202. doi: 10.1016/0952-3278(88)90170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A., Draznin B., Sussman K. E., Leitner J. W. Unmasking of arachidonate-induced insulin release by removal of extracellular calcium. Arachidonic acid mobilizes cellular calcium in rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 15;142(1):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90478-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A., Dunlop M. Stimulation of insulin release by phospholipase D. A potential role for endogenous phosphatidic acid in pancreatic islet function. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):427–435. doi: 10.1042/bj2700427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Ether-linked lysophospholipids initiate insulin secretion. Lysophospholipids may mediate effects of phospholipase A2 activation on hormone release. Diabetes. 1986 Jul;35(7):808–817. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.7.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Exogenous arachidonic acid promotes insulin release from intact or permeabilized rat islets by dual mechanisms. Putative activation of Ca2+ mobilization and protein kinase C. Diabetes. 1988 Nov;37(11):1453–1469. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.11.1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Glucose increases the synthesis of lipoxygenase-mediated metabolites of arachidonic acid in intact rat islets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):198–202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Metabolism of lysophospholipids in intact rat islets. The insulin secretagogue p-hydroxymercuribenzoic acid impairs lysophosphatidylcholine catabolism and permits its accumulation. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):863–869. doi: 10.1042/bj2410863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Pancreatic islet phospholipase A2: differential, Ca2+-dependent effects of lysophospholipids, arachidonic acid, and its lipoxygenase-derived metabolites on insulin release. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1987;17B:668–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Putative roles for lysophospholipids as mediators and lipoxygenase-mediated metabolites of arachidonic acid as potentiators of stimulus-secretion coupling: dual mechanisms of p-hydroxymercuribenzoic acid-induced insulin release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Sep;238(3):819–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. p-Hydroxymercuribenzoic acid inhibits arachidonic acid esterification into two distinct pools and stimulates insulin release in intact rat islets. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Sep;238(3):809–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Falke L. C., Gillis K., McDaniel M. L. A metabolite-regulated potassium channel in rat pancreatic B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell K. T., Ferrell J. E., Jr, Huestis W. H. Separation of phosphoinositides and other phospholipids by two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1986 Nov 1;158(2):447–453. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90574-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter-Riesch B., Fathi M., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B. Glucose and carbachol generate 1,2-diacylglycerols by different mechanisms in pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1154–1161. doi: 10.1172/JCI113430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pind S., Kuksis A. Further characterization of a novel phospholipase B (phospholipase A2--lysophospholipase) from intestinal brush-border membranes. Biochem Cell Biol. 1991 May-Jun;69(5-6):346–357. doi: 10.1139/o91-054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Biden T. J., Janjic D., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Wollheim C. B. Rapid mobilization of Ca2+ from rat insulinoma microsomes by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):562–564. doi: 10.1038/309562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Matschinsky F. M. Ca2+, cAMP, and phospholipid-derived messengers in coupling mechanisms of insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1185–1248. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajan A. S., Aguilar-Bryan L., Nelson D. A., Yaney G. C., Hsu W. H., Kunze D. L., Boyd A. E., 3rd Ion channels and insulin secretion. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):340–363. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P. Arachidonic acid metabolite regulation of insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1986;2(3-4):261–296. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P. Eicosanoids as pluripotential modulators of pancreatic islet function. Diabetes. 1988 Apr;37(4):367–370. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrey M. P., Montague W. Phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis in isolated guinea-pig islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 15;216(2):433–441. doi: 10.1042/bj2160433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearman M. S., Shinomura T., Oda T., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C subspecies in adult rat hippocampal synaptosomes. Activation by diacylglycerol and arachidonic acid. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80163-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomura T., Asaoka Y., Oka M., Yoshida K., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic action of diacylglycerol and unsaturated fatty acid for protein kinase C activation: its possible implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5149–5153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L. M., Holub B. J. Eicosanoid-dependent and -independent formation of individual [14C]stearoyl-labelled lysophospholipids in collagen-stimulated human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 4;1081(1):92–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90255-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Colca J. R., Kotagal N., McDaniel M. L. Arachidonic acid metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets. I. Identification and quantitation of lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 6;794(1):110–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90304-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Colca J. R., Kotagal N., McDaniel M. L. Arachidonic acid metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets. II. The effects of glucose and of inhibitors of arachidonate metabolism on insulin secretion and metabolite synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 6;794(1):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Colca J. R., McDaniel M. L. Arachidonic acid metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets. III. Effects of exogenous lipoxygenase products and inhibitors on insulin secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Mar 27;834(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Wolf B. A., Comens P. G., Colca J., Jakschik B., McDaniel M. L. Arachidonic acid metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets. IV. Negative ion-mass spectrometric quantitation of monooxygenase product synthesis by liver and islets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 14;835(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Wolf B. A., Lefkowith J. B., Stump W. T., McDaniel M. L. Glucose-induced phospholipid hydrolysis in isolated pancreatic islets: quantitative effects on the phospholipid content of arachidonate and other fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 5;879(3):399–409. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Wolf B. A., McDaniel M. L. Glucose-induced accumulation of inositol trisphosphates in isolated pancreatic islets. Predominance of the 1,3,4-isomer. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):259–263. doi: 10.1042/bj2370259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Wolf B. A., McDaniel M. L. The role of phospholipid-derived mediators including arachidonic acid, its metabolites, and inositoltrisphosphate and of intracellular Ca2+ in glucose-induced insulin secretion by pancreatic islets. Prog Lipid Res. 1987;26(2):125–181. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(87)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verspohl E. J., Tacke R., Mutschler E., Lambrecht G. Muscarinic receptor subtypes in rat pancreatic islets: binding and functional studies. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar 27;178(3):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90109-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Colca J. R., Turk J., Florholmen J., McDaniel M. L. Regulation of Ca2+ homeostasis by islet endoplasmic reticulum and its role in insulin secretion. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 1):E121–E136. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.2.E121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Comens P. G., Ackermann K. E., Sherman W. R., McDaniel M. L. The digitonin-permeabilized pancreatic islet model. Effect of myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate on Ca2+ mobilization. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):965–969. doi: 10.1042/bj2270965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Easom R. A., Hughes J. H., McDaniel M. L., Turk J. Secretagogue-induced diacylglycerol accumulation in isolated pancreatic islets. Mass spectrometric characterization of the fatty acyl content indicates multiple mechanisms of generation. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4291–4301. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Easom R. A., McDaniel M. L., Turk J. Diacylglycerol synthesis de novo from glucose by pancreatic islets isolated from rats and humans. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):482–490. doi: 10.1172/JCI114463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Florholmen J., Turk J., McDaniel M. L. Studies of the Ca2+ requirements for glucose- and carbachol-induced augmentation of inositol trisphosphate and inositol tetrakisphosphate accumulation in digitonin-permeabilized islets. Evidence for a glucose recognition site in insulin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3565–3575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Pasquale S. M., Turk J. Free fatty acid accumulation in secretagogue-stimulated pancreatic islets and effects of arachidonate on depolarization-induced insulin secretion. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 2;30(26):6372–6379. doi: 10.1021/bi00240a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Turk J., Sherman W. R., McDaniel M. L. Intracellular Ca2+ mobilization by arachidonic acid. Comparison with myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in isolated pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3501–3511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Regazzi R. Protein kinase C in insulin releasing cells. Putative role in stimulus secretion coupling. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):376–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81289-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Sharp G. W. Regulation of insulin release by calcium. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):914–973. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W. S., Rasmussen H. Control of insulin secretion: a model involving Ca2+, cAMP and diacylglycerol. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Apr 17;70(2):119–137. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


