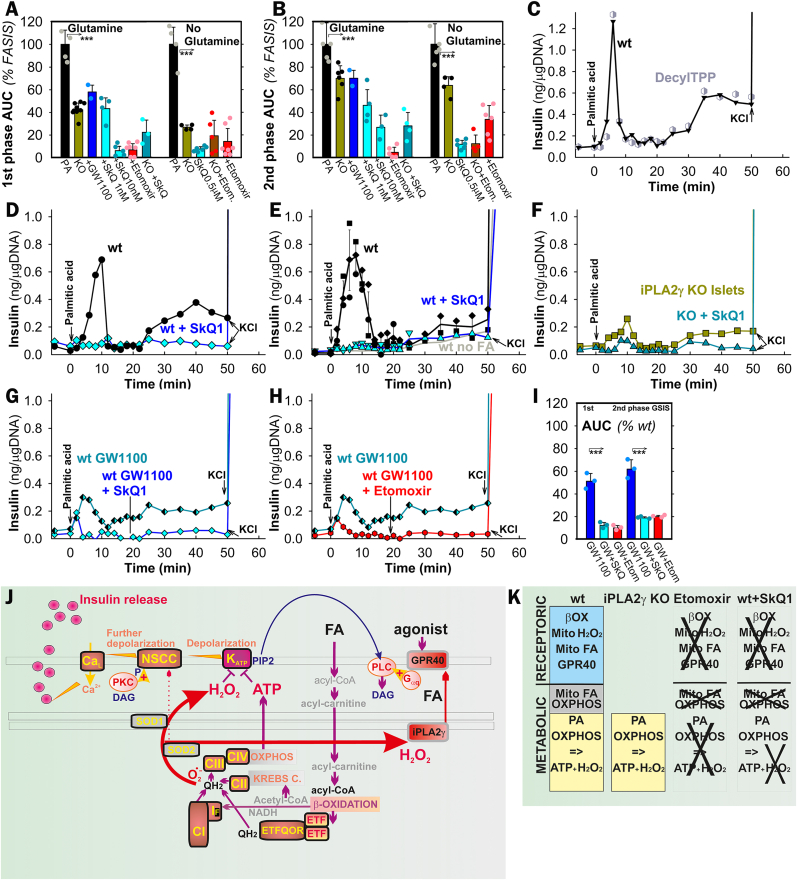
Fig. 2.
FASIS is prevented by mitochondria-targeted antioxidants SkQ1 A,B) To demonstrate the secreted insulin amounts, AUCs are quantified in ng/μg DNA for all measured perifusions under conditions of Fig. 1A plus those with 1 and 10 nM SkQ1 (cyan, dark cyan; “SkQ”), such as exemplified in traces of panels D–F with 10 nM SkQ1 (cyan, dark cyan) (D,F), or 0.5 μM SkQ1 (cyan) (E). The inactive SkQ1 mimics 10 nM DecylTPP was tested as illustrated in panel (C); as well as FASIS inhibition with 10 nM SkQ1 and 2.5 μM etomoxir on the top of 1 μM GW1100 was assayed as shown in panels G,H, while AUCs (N = 3) are summarized in panel I. ANOVA between groups is indicated: **p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001. (J) Scheme of working hypothesis: redox signaling from mitochondria to the plasma membrane and intra-mitochondrial redox signaling upon FASIS. CI–CIV are respiratory chain complexes (a superoxide-forming flavin site is denoted IF); ETFQOR is ETF:ubiquinone-oxidoreductase; DAG stands for diacylglycerols; NSCC for nonspecific calcium channels, such as TRPM channels; „PIP2″, i.e. PIP2 is phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, required to be unbound from KATP to release its permanent opening. K) Contribution of various components to insulin release upon FASIS.