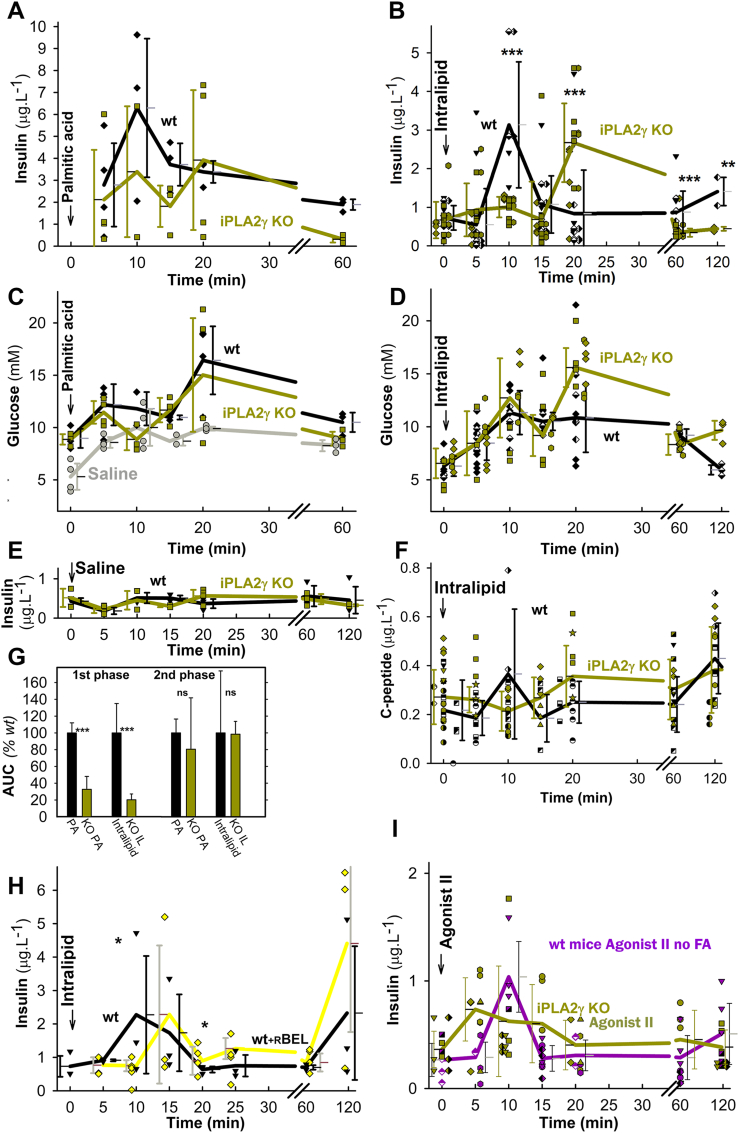
Fig. 8.
Insulin and c-peptide in blood and glycemia after i.p. administration of palmitic acid and Intralipid
Backcrossed wt mice: black; iPLA2γKO mice: green.
Palmitic acid (100 mg kg−1; left panels A,C,G; N = 10, n = 20 for wt or KO; n = 20 for C), Intralipid (7.5 μl g−1; right panels B,D,F,G; N = 40, n = 98 for wt or N = 40, n = 81 for KO in B,D; or saline only (E; gray trace in C) were i.p. injected at time zero. AUCs normalized to wt are also shown (G), while SDs were derived from AUCs of given time point values + SDs or –SDs. ANOVA: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Each mouse was sampled for blood insulin and glycemia two to three times and time courses were constructed from different times of different mice. The groups of mice investigated are indicated with different symbols. H) wt mice pretreated with 1 mg kg−1r-BEL (yellow; N = 15, n = 30) are compared to wt controls (black; N = 42, n = 84). I) Insulin in blood after i.v. administration of Agonist II in mice– Backcrossed wt mice: violet, N = 18, n = 37; iPLA2γKO mice: green, N = 19, n = 41. After Agonist II (10 μmol kg−1) i.v. administration, each mouse was sampled two to three times for blood insulin and glycemia (glycemia, AUCs, see Supplementary Information Figs. S8D–G) and a time course was constructed from different times of different mice. Groups of mice investigated are indicated by different symbols.