Figure 3.
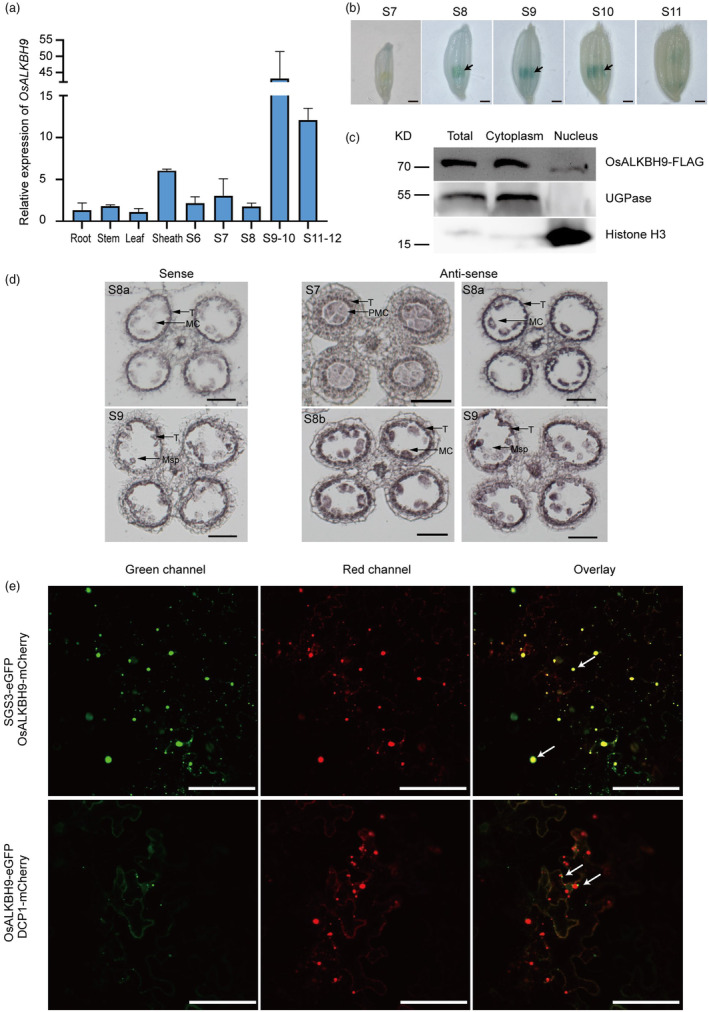
OsALKBH9 is highly expressed in anthers and OsALKBH9 is mainly localized in cytoplasm. (a) Expression analysis of OsALKBH9 in different tissues by qRT‐PCR. Anthers were collected at developmental stage 6 to stage 12. Other tissues were harvested from plants at the flowering stage. S6, stage 6; S7, stage 7; S8, stage 8; S9–10, stage 9 to stage 10; S11–12, stage 11 to stage 12. (b) GUS staining of transgenic anthers containing OsALKBH9pro::GUS. Scale bars, 1 mm. Arrows pointing anthers with strong GUS signals. S7, stage 7; S8, stage 8; S9, stage 9; S10, stage 10; S11, stage 11. (c) Subcellular fraction and immunoblot assay. Total protein, cytoplasm, and nuclei‐enriched fractions from Osalkbh9‐1 OsALKBH9pro::OsALKBH9CDS‐FLAG transformants are subject to SDS‐PAGE. UGPase and Histone H3 are used as cytoplasmic and nuclear markers, respectively. (d) In situ hybridization of OsALKBH9 transcripts in WT anthers. S7, stage 7; S8a, stage 8a; S8b, stage 8b; S9, stage 9. T, tapetum; PMC, pollen mother cell; MC, meiotic cell; Msp, microspore. Scale bars, 50 μm. (e) Subcellular localization of OsALKBH9 in N. benthamiana leaves epidermal cells. Arrows pointing co‐localized foci of OsALKBH9‐mCherry and SGS3‐eGFP (the upper panel), and non‐co‐localized foci of OsALKBH9‐eGFP and DCP1‐mCherry (the lower panel). Scale bars, 100 μm.
