Fig. 4. ATF4 and NRF2 coordinately regulate Slc7a11 expression.
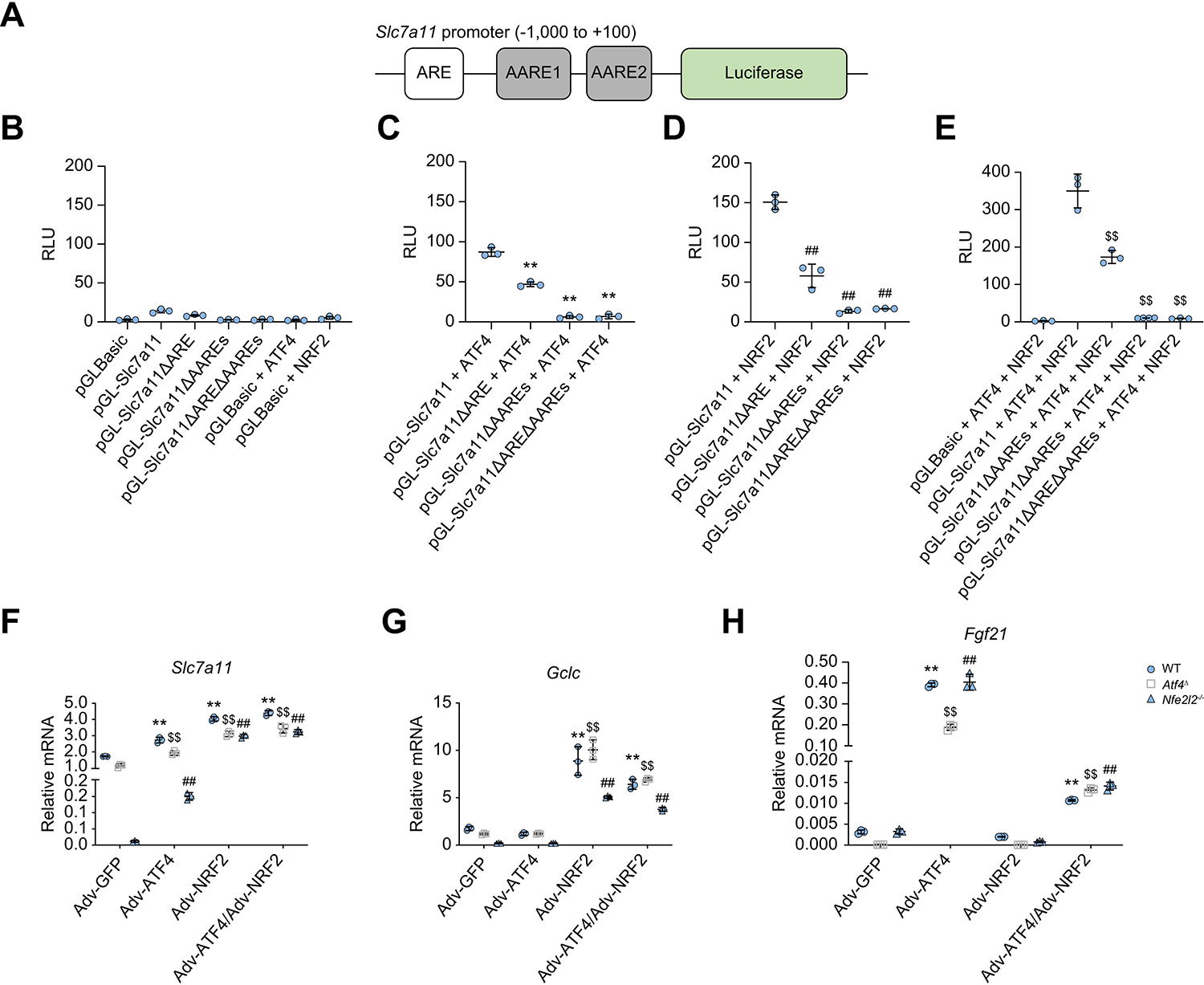
(A) Schematic representation of the mouse Slc7a11 gene promoter with the upstream ARE and the two AAREs (AARE-1 and AARE-2) indicated by open and solid rectangles, respectively, fused to a luciferase reporter. (B–E) Luciferase assay measuring Slc7a11 promoter activity before and after ARE and AARE deletion (ΔARE, ΔAAREs, and ΔAREΔAAREs) in the absence (B) or presence of ATF4 (C), NRF2 (D), and ATF4 + NRF2 (E). HEK293 cells were cotransfected with reporter plasmids (pGLBasic, pGL-Slc7a11, and its variants) in combination with pAd-track-NRF2 and/or ATF4 expression vectors, and a control Renilla luciferase vector PRL-TK. After 24 h, luciferase activities were measured and normalised to Renilla luciferase activity and presented as RLU (mean ± SD from three independent experiments). **p <0.01 (vs. pGL-Slc7a11 + ATF4); ##p <0.01 (vs. pGL-Slc7a11 + NRF2); $$p <0.01 (vs. pGL-Slc7a11 + ATF4 + NRF2), Student’s t test. (F–H) qRT-PCR analysis of Slc7a11 (F), Gclc (G), and Fgf21 (H) mRNAs in WT, Atf4Δ, and Nfe2l2−/− hepatocytes transduced with Adv-GFP, Adv-ATF4, Adv-NRF2, or Adv-ATF4 + NRF2. Mean ± SD (n = 3/group). **p <0.01 (vs. Adv-GFP of WT hepatocytes); $$p <0.01 (vs. Adv-GFP of Atf4Δ hepatocytes); ##p <0.01 (vs. Adv-GFP of Nfe2l2−/− hepatocytes), Student’s t test. AARE, amino acid response element; Adv, adenovirus; ARE, antioxidant response element; ATF4, activating transcription factor 4; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse-transcription PCR; RLU, relative luminescence unit; SLC7A11, solute carrier family 7a member 11; WT, wild-type.
