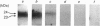Abstract
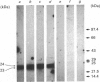
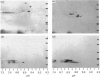
As a first step in determining the molecular mechanism of membrane fusion stimulated by GTP in rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), we have looked for GTP-binding proteins. Rough microsomes from rat liver were treated for the release of ribosomes, and the membrane proteins were separated by SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. The polypeptides were then blotted on to nitrocellulose sheets and incubated with [alpha-32P]GTP [Bhullar & Haslam (1987) Biochem. J. 245, 617-620]. A doublet of polypeptides (23 and 24 kDa) was detected in the presence of 2 microM-MgCl2. Binding of [alpha-32P]GTP was blocked by 1-5 mM-EDTA, 10-10,000 nM-GTP or 10 microM-GDP. Either guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate or guanosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate at 100 nM completely inhibited binding, but ATP, CTP or UTP at 10 mciroM did not. Pretreatment of microsomes by mild trypsin treatment (0.5-10 micrograms of trypsin/ml, concentrations known not to affect microsomal permeability) led to inhibition of [alpha-32P]GTP binding, suggesting a cytosolic membrane orientation for the GTP-binding proteins. Two-dimensional gel-electrophoretic analysis revealed the 23 and 24 kDa [alpha-32P]GTP-binding proteins to have similar acid isoelectric points. [alpha-32P]GTP binding occurred to similar proteins of rough microsomes from rat liver, rat prostate and dog pancreas, as well as to a 23 kDa protein of rough microsomes from frog liver, but occurred to distinctly different proteins in a rat liver plasma-membrane-enriched fraction. Thus [alpha-32P]GTP binding has been demonstrated to two low-molecular-mass (approx. 21 kDa) proteins in the rough endoplasmic reticulum of several varied cell types.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audigier Y., Nigam S. K., Blobel G. Identification of a G protein in rough endoplasmic reticulum of canine pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16352–16357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Two roles for guanine nucleotides in the stimulus-secretion sequence of neutrophils. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):504–507. doi: 10.1038/319504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudhuin P., Evrard P., Berthet J. Electron microscopic examination of subcellular fractions. I. The preparation of representative samples from suspensions of particles. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jan;32(1):181–191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckers C. J., Balch W. E. Calcium and GTP: essential components in vesicular trafficking between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1245–1256. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhullar R. P., Haslam R. J. Detection of 23-27 kDa GTP-binding proteins in platelets and other cells. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):617–620. doi: 10.1042/bj2450617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calés C., Hancock J. F., Marshall C. J., Hall A. The cytoplasmic protein GAP is implicated as the target for regulation by the ras gene product. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):548–551. doi: 10.1038/332548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comerford J. G., Dawson A. P. The effect of limited proteolysis on GTP-dependent Ca2+ efflux and GTP-dependent fusion in rat liver microsomal vesicles. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 15;258(3):823–829. doi: 10.1042/bj2580823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comerford J. G., Dawson A. P. The mechanism of action of GTP on Ca2+ efflux from rat liver microsomal vesicles. Measurement of vesicle fusion by fluorescence energy transfer. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):89–93. doi: 10.1042/bj2490089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson A. P. GTP enhances inositol trisphosphate-stimulated Ca2+ release from rat liver microsomes. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):147–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80759-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. L., Ueda T., Chueh S. H., Noel M. W. Ca2+ release from endoplasmic reticulum is mediated by a guanine nucleotide regulatory mechanism. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):461–464. doi: 10.1038/320461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godelaine D., Beaufay H. The membrane of the rough endoplasmic reticulum contains cytoplasmically exposed high affinity GTP-binding sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 14;148(1):478–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godelaine D., Beaufay H., Wibo M. Incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine into endogenous acceptors of rough microsomes from rat liver: stimulation by GTP after treatment with pyrophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1095–1099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godelaine D., Beaufay H., Wibo M., Ravoet A. M. Alteration of membrane barrier in stripped rough microsomes from rat liver on incubation with GTP: its relevance to the stimulation by this nucleotide of the dolichol pathway for protein glycosylation. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):340–350. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Salminen A., Walworth N. C., Novick P. J. A GTP-binding protein required for secretion rapidly associates with secretory vesicles and the plasma membrane in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):753–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock K., Tsang V. C. India ink staining of proteins on nitrocellulose paper. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henne V., Piiper A., Söling H. D. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and 5'-GTP induce calcium release from different intracellular pools. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 22;218(1):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Wall D. A., Ma A. Isolation of rat hepatocyte plasma membranes. I. Presence of the three major domains. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):217–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C., Chen L. B. Dynamic behavior of endoplasmic reticulum in living cells. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D., Reggio H., Warren G. Antibodies to the Golgi complex and the rough endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):92–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Glick B. S., Malhotra V., Weidman P. J., Serafini T., Gleason M. L., Orci L., Rothman J. E. Involvement of GTP-binding "G" proteins in transport through the Golgi stack. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos M., Jr, Nguyen N. Y., Liu T. Y. Reproducible high yield sequencing of proteins electrophoretically separated and transferred to an inert support. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6005–6008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicchitta C. V., Joseph S. K., Williamson J. R. GTP-mediated Ca2+ release in rough endoplasmic reticulum. Correlation with a GTP-sensitive increase in membrane permeability. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):741–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2480741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paiement J., Beaufay H., Godelaine D. Coalescence of microsomal vesicles from rat liver: a phenomenon occurring in parallel with enhancement of the glycosylation activity during incubation of stripped rough microsomes with GTP. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):29–37. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paiement J., Bergeron J. J. Localization of GTP-stimulated core glycosylation to fused microsomes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1791–1796. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paiement J., Kan F. W., Lanoix J., Blain M. Cytochemical analysis of the reconstitution of endoplasmic reticulum after microinjection of rat liver microsomes into Xenopus oocytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Oct;36(10):1263–1273. doi: 10.1177/36.10.2843593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paiement J. Physiological concentrations of GTP stimulate fusion of the endoplasmic reticulum and the nuclear envelope. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Apr;151(2):354–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90386-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paiement J., Rindress D., Smith C. E., Poliquin L., Bergeron J. J. Properties of a GTP sensitive microdomain in rough microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Mar 26;898(1):6–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paiement J., Roy L. Electrophoretic protein blots as aids in choosing fixatives for immunocytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Apr;36(4):441–446. doi: 10.1177/36.4.2450122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Austen B. GTP-dependent ADP-ribosylation of a 22 kDa protein in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 22;218(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Novick P. J. A ras-like protein is required for a post-Golgi event in yeast secretion. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev N., Mulholland J., Botstein D. The yeast GTP-binding YPT1 protein and a mammalian counterpart are associated with the secretion machinery. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90433-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields D., Blobel G. Cell-free synthesis of fish preproinsulin, and processing by heterologous mammalian microsomal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2059–2063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sribney M., Dove J. L., Lyman E. M. Studies on the synthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol: stimulation by GTP and inhibition by ATP and fluoride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 7;79(3):749–755. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Unkeless J. C. Partial purification of a lipoprotein with 5'-nucleotidase activity from membranes of rat liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):1050–1057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Connolly T., Morrison T., Gilmore R. Integration of membrane proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum requires GTP. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):69–77. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]