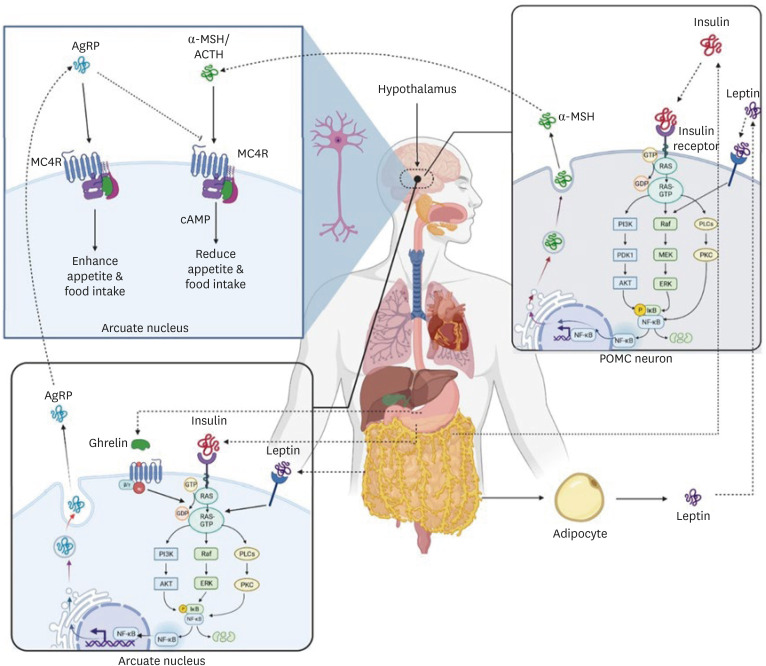
Figure 1. α-MSH and AgRP control food consumption and energy intake by stimulation and inhibition of the melanocortin 4 receptor. MC4R is stimulated by α-MSH, which reduces appetite and food intake. In contrast, AgRP inhibits MC4R and increases food intake. Leptin secreted by adipocytes that decreases food intake by acting on anorectic POMC neurons and stimulating α-MSH in the hypothalamus. Insulin secreted by beta cells in the pancreas and stimulates α-MSH secretion through a pathway similar to leptin. In contrast, Ghrelin sends signals to AgRP neurons and stimulates the secretion of AgRP. Ghrelin is released during hunger from the gastrointestinal tract and increases appetite.
AgRP, agouti-related protein; α-MSH, α-melanocyte stimulating hormone; ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone MC4R, melanocortin 4 receptor; NF, nuclear factor; POMC, pro-opiomelanocortin.