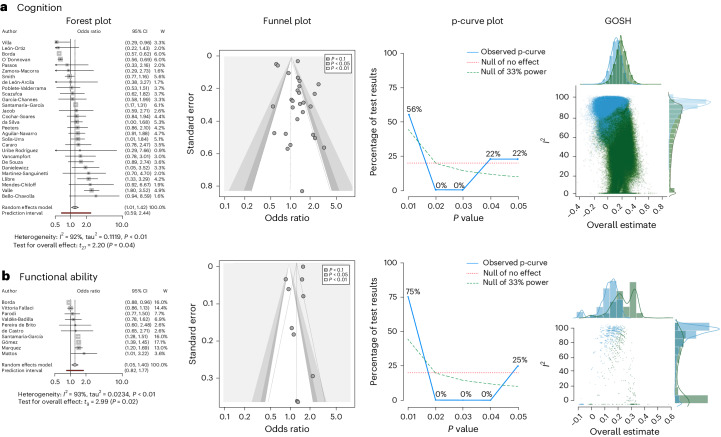
Fig. 3. Meta-analysis across all risk factors for cognition and functional ability.
a, Cognition. Forest plot shows k studies in random effects model (first author, OR, CI and weights). The random effects model results (cognition: k = 28, n = 102,064, OR = 1.2006, P = 0.0363, CI = (1.0127, 1.4234); functional ability: k = 10, n = 99,428, OR = 1.2088, P = 0.0153, CI = (1.0470, 1.3956)) are reported with Knapp–Hartung correction for false discovery rate, the prediction interval and heterogeneity values (I2 and tau2). W, weights. b, Functional ability. Forest plot shows k studies in random effects model (first author, OR, CI and weights). The random effects model results (functional ability: k = 10, n = 99,428, OR = 1.2088, P = 0.0153, CI = (1.0470, 1.3956)) are reported with Knapp–Hartung correction for false discovery rate, the prediction interval and heterogeneity values (I2 and tau2). For a and b, contour-enhanced funnel plot shows effect sizes, standard errors and significance; p-curve analysis shows the accumulation of P values over the significant studies (observed p-curve), the no-effect curve and 33% power curve; and the GOSH shows distribution for all 2k−1 possible study combinations (1 million randomly selected models when 2k−1 > 106) in blue and leaving out the most negatively influential study in green.