Table 5.
Recommendations for surgical ablation
| COR | LOE | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
1. For patients with AF who are undergoing cardiac surgery, concomitant surgical ablation is beneficial to reduce the risk of recurrent AF |
 |
 |
2. In patients undergoing surgical ablation, anticoagulation is reasonable for at least 3 months after the procedure to reduce thromboembolic risk |
 |
 |
3. For patients with symptomatic persistent AF refractory to antiarrhythmic drug therapy, hybrid epicardial and endocardial ablation might be reasonable to reduce the risk of recurrent atrial tachyarrhythmia |
COR Class (Strength) of recommendation
LOE Level (Quality) of evidence
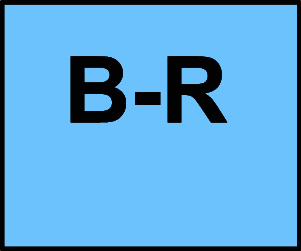
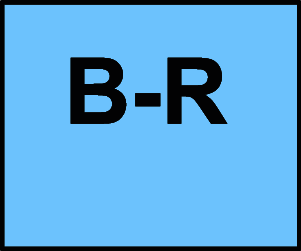
B-R Moderate-quality evidence from 1 or more randomized controlled trials (RCTs); Meta-analyses of moderate-quality RCTs
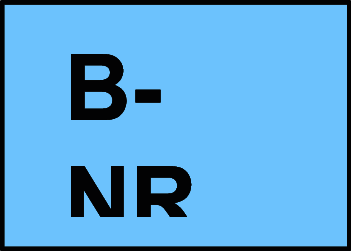
B-NR Data derived from nonrandomized trials
AF atrial fibrillation
Adapted from reference 3, with permission
