Abstract
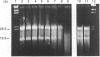
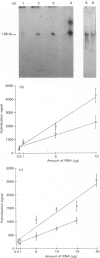
Inclusion of aurintricarboxylic acid (ATA) in extraction buffers for the isolation of RNA from animal tissues resulted in high yields (0.5-2.0 mg/g of tissue) of undegraded material as judged by agarose-gel-electrophoretic analyses and Northern-blotting experiments. However, ATA bound to nucleic acids, forming stable complexes, and so we have established methods for spectrophotometric quantification of RNA in these coloured complexes, and for easy removal of sufficient ATA to leave RNA in a consistently hybridizable condition at the end of a purification. The use and subsequent removal of ATA was straightforward and gave satisfactory results for all rat tissues tested.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González R. G., Blackburn B. J., Schleich T. Fractionation and structural elucidation of the active components of aurintricarboxylic acid, a potent inhibitor of protein nucleic acid interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 24;562(3):534–545. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González R. G., Haxo R. S., Schleich T. Mechanism of action of polymeric aurintricarboxylic acid, a potent inhibitor of protein--nucleic acid interactions. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 2;19(18):4299–4303. doi: 10.1021/bi00559a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallick R. B., Chelm B. K., Gray P. W., Orozco E. M., Jr Use of aurintricarboxylic acid as an inhibitor of nucleases during nucleic acid isolation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3055–3064. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles M. F., Hung P., Jungmann R. A. Cyclic AMP regulation of lactate dehydrogenase. Quantitation of lactate dehydrogenase M-subunit messenger RNA in isoproterenol-and N6,O2'-dibutyryl cyclic AMP-stimulated rat C6 glioma cells by hybridization analysis using a cloned cDNA probe. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12545–12552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz-Harder B., Tata J. R. Inhibition of nuclear ribonuclease activity during transcription in vitro by aurintricarboxylic acid and vanadyl riboncleoside complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 11;104(3):903–910. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91334-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]