Fig 1.
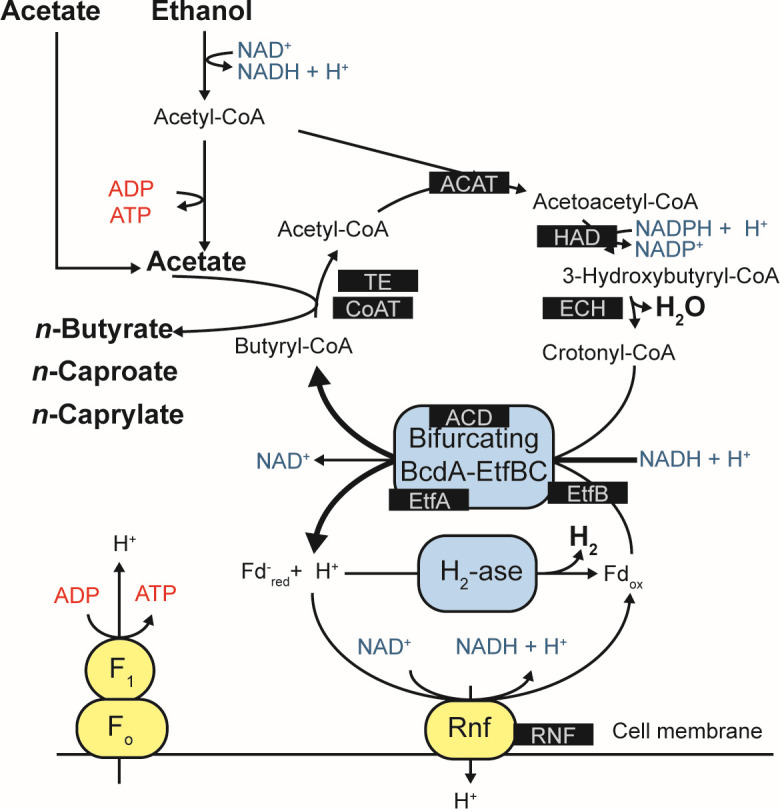
The RBOX pathway investigated in this study. The enzymes we examined in this study are highlighted in black boxes. The figure was modified with permission from Angenent et al. (21). RBOX pathway enzymes are ACAT, acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase (Thiolase II); HAD, 3-hydroxy-acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; ECH, enoyl-CoA dehydratase; ACD, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; EtfA/B, electron-transfer-flavoprotein subunit A/B; CoAT, acetyl CoA-transferase; TE, thioesterase; RNF, Rnf respiratory complex.
