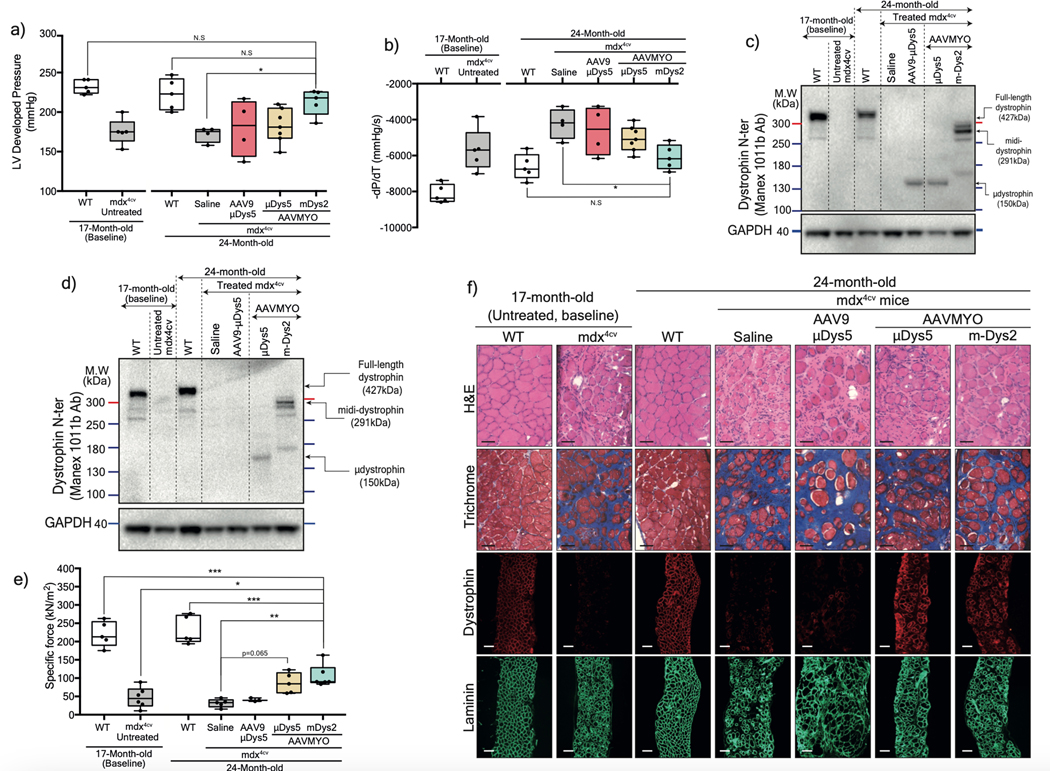
Figure 6: Protection of heart and diaphragm muscles of old mdx4cv mice with dual AAVMYO midi-Dys approach.
Cardiac function was assessed ex vivo using isolated and perfused hearts in the Langendorf chamber. a) Left ventricle developed pressure and b) negative rate of pressure change measured 5min following high workload induction by high calcium concentration. For a and b, Saline and AAV9-μDys: n=4, WTs, untreated, and AAVMYO mDys2: n=5, AAVMYO μDys: n=6. Western blot analysis of c) heart or d) diaphragm lysates showing a successful assembly and enrichment of midi-Dys2 in heart and diaphragm muscles following a long-term treatment AAV low dose (total dose: 2×1013 vg/kg). e) Plots representing the maximal force measured in vitro using diaphragm strips from WT or mdx4cv mice (AAV9-μDys: n=4, WTs, Saline, and AAVMYO μDys: n=5, AAVMYO midiDys2: n=6). f) H&E, Trichrome staining (Scale bar: 50 μm), or double-immunolabeling (Scale bar: 100 μm) of dystrophin and laminin of diaphragm cross-sections. Data represent means±s.e.m. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001. (ANOVA test followed by Tukey’s post hoc).