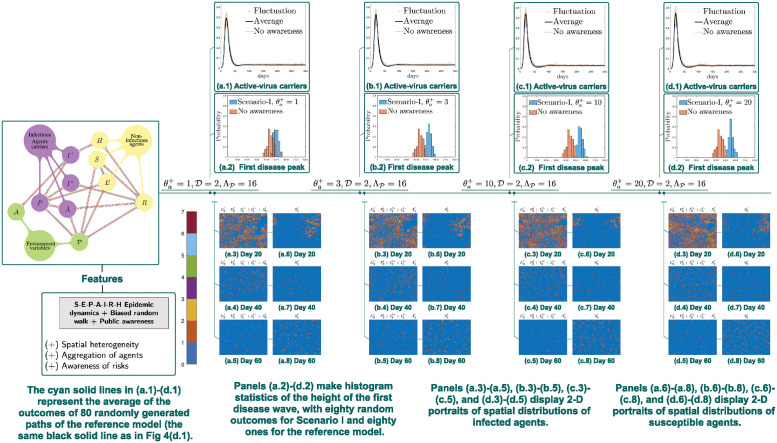
Fig 5. Simulations of Scenario I: Integrating awareness into biasness of random walks.
Panels (a.1)-(d.1) compare , where the reference is the biased random walk model without awareness in Section 2.4. Incorporated awareness in biasness alone does not necessarily constrain outbreaks. When the increment of public awareness increases from 1 to 3 to 10 to 20, there is a high chance that the susceptible agents have already transitioned into the exposed or asymptomatic infectious ones. As a result, disease transmissions are boosted and outbreaks are escalated.