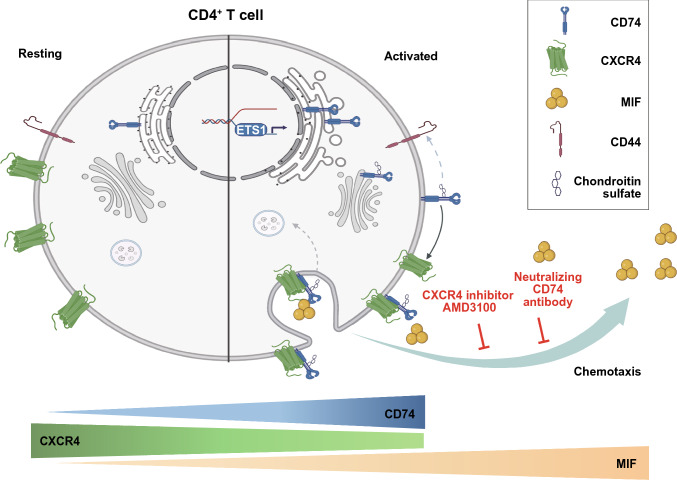
Fig. 7.
Scheme of the regulation of the MIF receptors CD74 and CXCR4 in resting and activated CD4+ T-cell state. During resting state, CD4+ T cells express CXCR4 abundantly on the cell surface, while CD74 is constitutively expressed and synthesized intracellularly. Most likely due to its retention signal CD74 resides in the ER with functional circulation in the endolysosomal compartment. Triggered by T-cell activation, CD74 gene expression and protein synthesis is rapidly upregulated in contrast to the initially repressed CXCR4 expression. We speculate, that ETS1 might be involved in the rapid regulation of CD74 in this process. Furthermore, CD74 molecules are post-translationally modified by addition of chondroitin sulfate moieties. This modification enables rapid transport of CD74 towards the cell surface, where it can act as a functional surface receptor for MIF, a proinflammatory cytokine that is secreted during T-cell activation and exerts additional auto- and paracrine effects. In activated CD4+ T cells, MIF leads to internalization of CD74/CXCR4 receptor complexes. Both receptors are crucial for MIF-induced chemotaxis, as blockade of either CXCR4 or CD74 abrogates CD4+ T-cell migration towards MIF. Scheme was created with BioRender.com (license of the Institute for Stroke and Dementia Research)