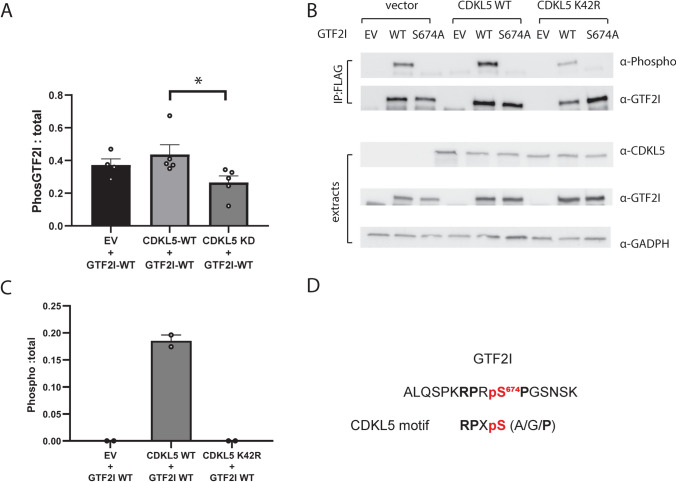
Fig. 6.
Orthogonal validation approach to demonstrate that CDKL5 phosphorylates GTF2I at Ser674 in human cells. A Quantification of three independent experiments showed a significant difference in the phosphorylation levels in GTF2I when co-expressed with CDKL5 WT compared to either empty vector (EV) or CDKL5 kinase dead (K42R) mutant. Site-directed mutagenesis of GTF2I at Ser674 to Ala (SA) completely abolished phosphorylation levels and was not quantifiable. Data is representative of 5 independent samples from 5 independent experiments. Data is mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05. B Lysate extract sets from co-transfection experiments were probed with anti-CDKL5 (top panel), anti-GTF2I (middle panel) and anti-GAPDH (bottom panel). Five independent experiments were completed and the expression patterns indicate that the co-transfection experiments were successful. Data is mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. C Phosphorylation of GTF2I WT was only detected in HEK293T cells co-transfected with CDKL5 WT compared to co-transfected with CDKL5 K42R or empty vector. Phospho-peptides were quantified using LC–MS/MS intensity of phosphopeptides was normalised to the label-free quantification of GTF2I. The phosphorylation event was detected in two of six independent experiments. D Phosphopeptide detected from GTF2I that is phosphorylated by CDKL5