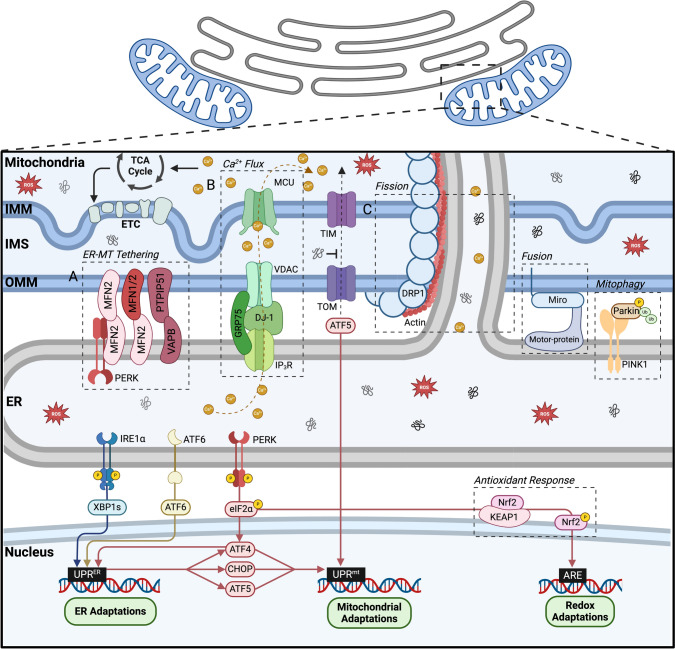
Fig. 3.
Mitochondria-ER contact sites molecular components and cellular functions. MERCS are relatively stable structures that require the formation of molecular bridges established by interacting proteins anchored in the smooth ER and the OMM [5]. Tethering complexes are essential, structural and reversible bonds that stabilise MERCS [177]. A MERCS tethering complexes occur between ER MFN2 and mitochondrial MFN2 or ER MFN2 and MFN1 [178]. The MFN tethering complex is dependent on the interaction of MFN2 and PERK at the ER membrane, essential for the establishment of the contact sites [90, 179]. Other complexes reported as regulating the tethering of MERCS include the ER VAPB and the OMM PTPIP51 [180]. B MERCS regulate Ca2+ flux between the ER and the mitochondria by the complex that forms between IP3R from the ER and VDAC from the OMM [5, 177]. Ca2+ passes through the MCU to reach the mitochondrial matrix [185, 186]. DJ-1 [187] and GRP75 [188] regulate the connection between IP3R and VDAC [189]. Some components of the TCA cycle require the binding of Ca2+ for their function, the interaction of mitochondria and ER via MERCS supply Ca2+ to mitochondria for stimulating the TCA cycle, resulting in an increase in ATP production [190]. C MERCS control the processes of mitochondrial fusion, fission and mitophagy [111, 191]. The ER promotes the polymerisation of actin filaments and establishment of close contacts between the two organelles [192]. ER tubules will release Ca2+ ions into the mitochondria, triggering the inner mitochondrial membrane to divide [192, 193]. DRP1 assembles around mitochondria at the fission site, a DRP1 ring constricts with the aid of actin–myosin filaments, resulting in the formation of two daughter mitochondria. ER tubules guide the position and timing of mitochondria fusion through the tethering with mitochondria [191, 194]. During mitochondrial fusion the contact sites between the tubules and the mitochondria need to be maintained to avoid the disruption of these MERCS, the Ca2+ sensitive motorprotein Miro cease all transportation movements of the mitochondria involved [195]. In the mitochondria PINK1 phosphorylates MFN2, recruits Parkin at the MERCS, allowing Parkin dependent ubiquitination of ER MFN2, promoting the separation of the two organelles and the initiation of mitophagy [196]