Fig. 4.
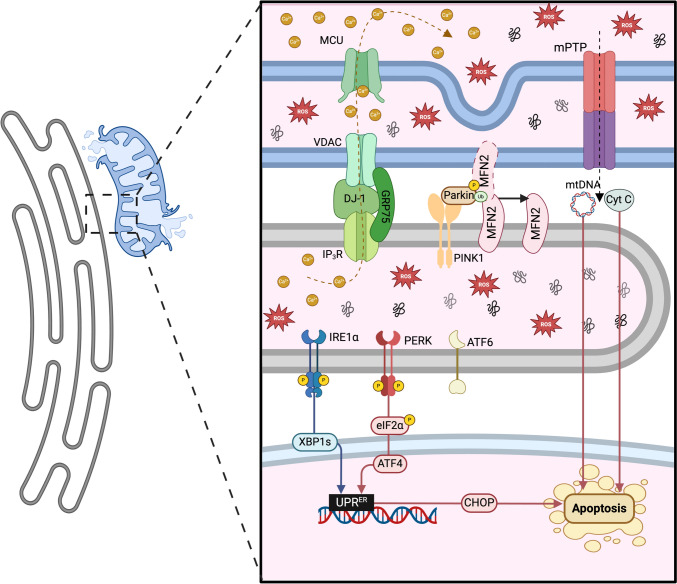
MERCS regulation of cellular signalling in ageing and disease. Disruption of MERCS assembly and disassembly plays a key role in pathophysiological conditions particularly in ageing and age-related diseases. Disrupted Ca2+ flow from the ER to mitochondria can result in mitochondrial dysfunction with loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and mitochondrial ROS generation, that result in activation of apoptotic pathways or senescence [40]. Excess Ca2+ transfer into mitochondria via IP3R can induce the opening of the mPTP, release of cytochrome c and activation of the caspase signalling cascade and pro-apoptotic pathways [198]. On mitochondria PINK1 phosphorylates MFN2, recruits Parkin at the MERCS, allowing Parkin dependent ubiquitination of ER MFN2, promoting the separation of the two organelles and the initiation of mitophagy [196]. Release of mtDNA through channels such as VDAC (located in or close to MERCS) has emerged as a potential regulator for the inflammatory response [201]