Abstract
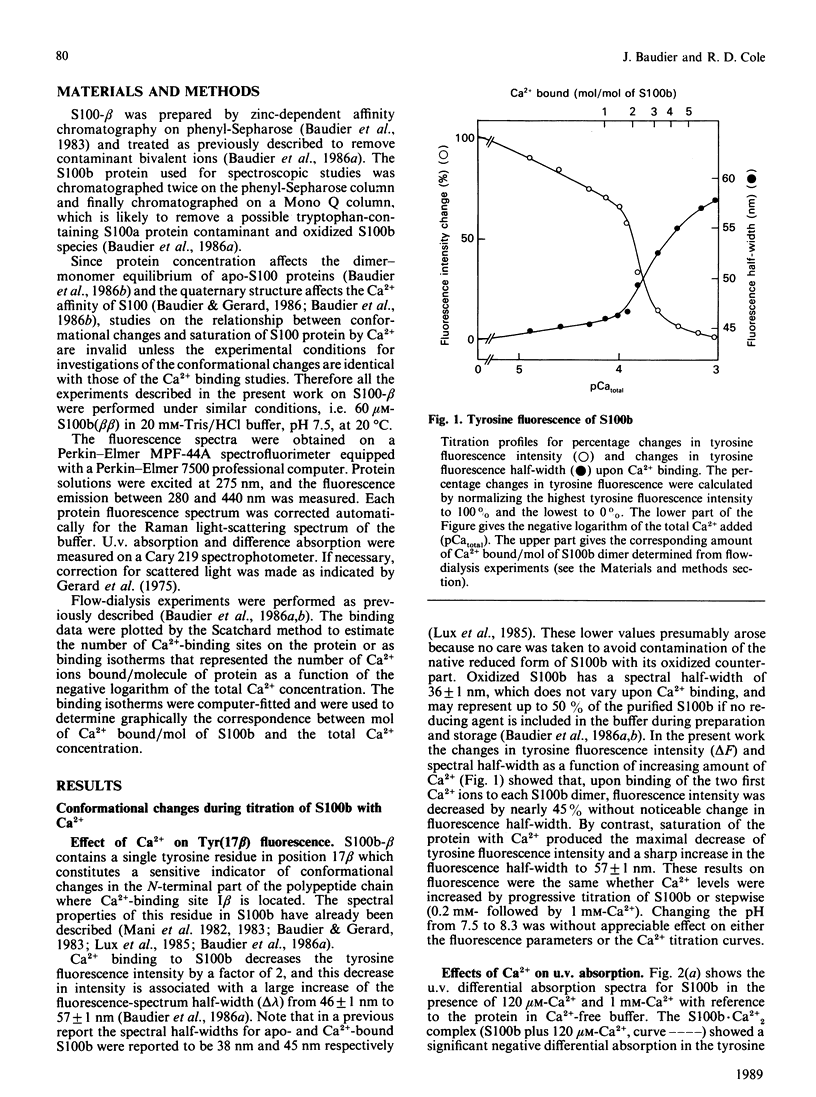
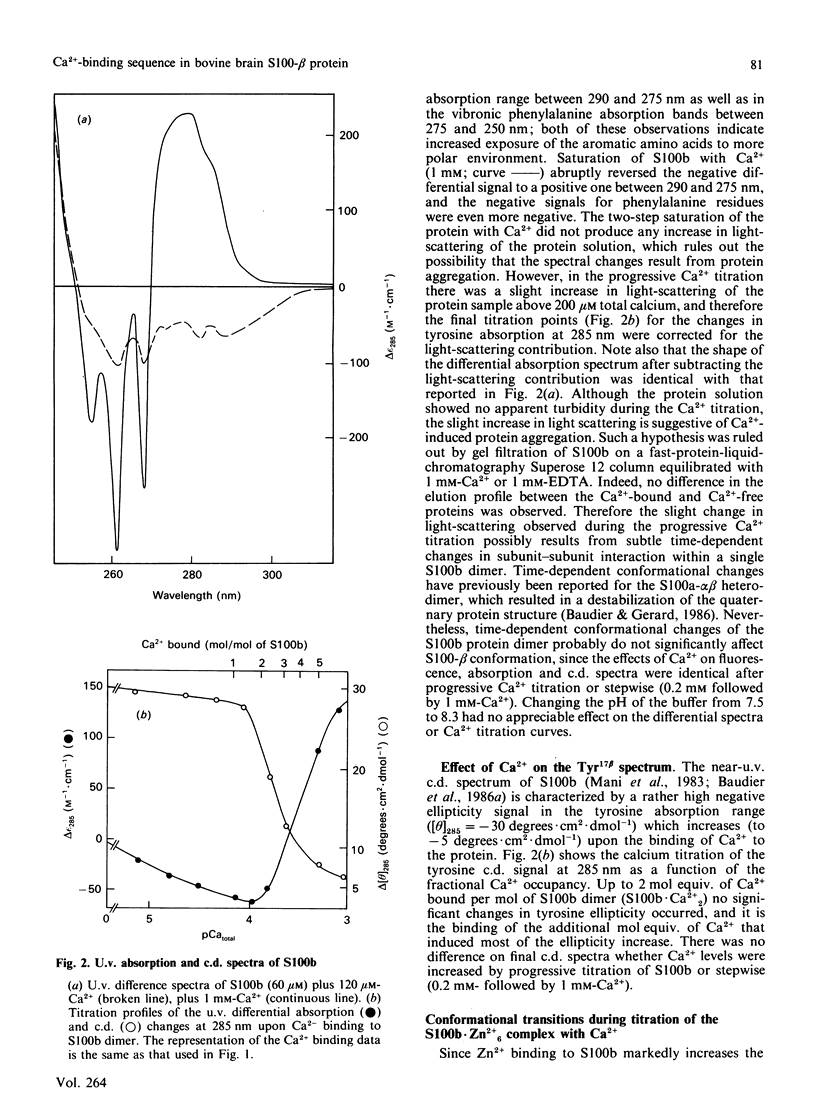
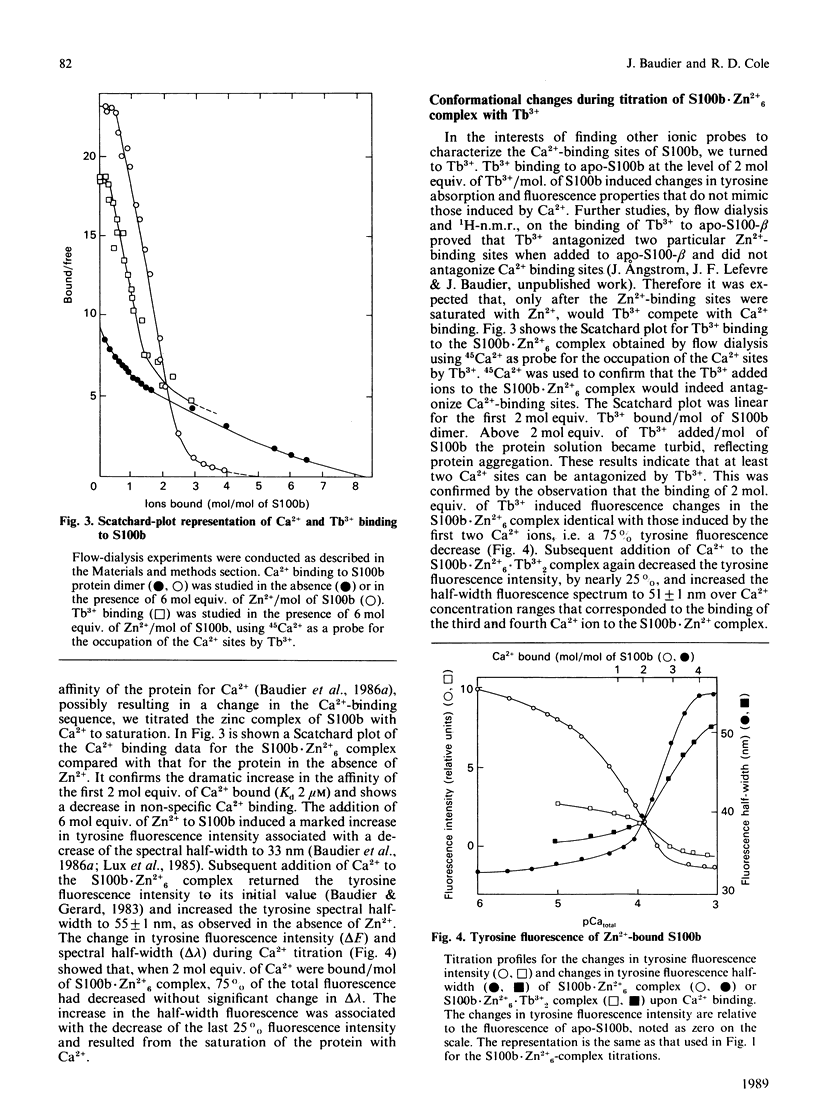
Conformational changes in the beta-subunit of the bovine brain Ca2+-binding protein S100b (S100-beta) accompanying Ca2+ binding were investigated by analysis of the spectroscopic properties of the single tyrosine residue (Tyr17 beta) and flow-dialysis binding experiments. S100-beta binds Ca2+ sequentially at two sites to change the conformation of the protein. The first Ca2+ ion binds to site II beta, a typical Ca2+-binding site in the C-terminal region, and it does not significantly perturb the proximal environment of Tyr17 beta. After the first site is occupied, another Ca2+ ion binds to the N-terminal Ca2+-binding site, I beta, and strengthens a hydrogen bond between Tyr17 beta and a neighbouring carboxylate acceptor group, which results in a large increase in the Tyr17 beta fluorescence spectrum half-width and a positive absorption and c.d. signal between 290 and 275 nm. Ca2+ binding to the S100b.Zn2+6 complex, studied by flow-dialysis and fluorescence measurements showed that, although Zn2+ ions increase the affinity of S100b protein for Ca2+, the Ca2+-binding sequence was not changed. Tb3+ (terbium ion) binding studies on the S100b.Zn2+6 complex proved that Tb3+ antagonizes only Ca2+ binding site II beta and confirmed the sequential occupation of Ca2+-binding sites on the S100b.Zn2+6 complex.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babu Y. S., Sack J. S., Greenhough T. J., Bugg C. E., Means A. R., Cook W. J. Three-dimensional structure of calmodulin. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):37–40. doi: 10.1038/315037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Cole R. D. Reinvestigation of the sulfhydryl reactivity in bovine brain S100b (beta beta) protein and the microtubule-associated tau proteins. Ca2+ stimulates disulfide cross-linking between the S100b beta-subunit and the microtubule-associated tau(2) protein. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2728–2736. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Gerard D. Ions binding to S100 proteins. II. Conformational studies and calcium-induced conformational changes in S100 alpha alpha protein: the effect of acidic pH and calcium incubation on subunit exchange in S100a (alpha beta) protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8204–8212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Glasser N., Duportail G. Bimane- and acrylodan-labeled S100 proteins. Role of cysteines-85 alpha and -84 beta in the conformation and calcium binding properties of S100 alpha alpha and S100b (beta beta) proteins. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6934–6941. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Glasser N., Gerard D. Ions binding to S100 proteins. I. Calcium- and zinc-binding properties of bovine brain S100 alpha alpha, S100a (alpha beta), and S100b (beta beta) protein: Zn2+ regulates Ca2+ binding on S100b protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8192–8203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Gérard D. Ions binding to S100 proteins: structural changes induced by calcium and zinc on S100a and S100b proteins. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 5;22(14):3360–3369. doi: 10.1021/bi00283a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Holtzscherer C., Gerard D. Zinc-dependent affinity chromatography of the S100b protein on phenyl-Sepharose. A rapid purification method. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 8;148(2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80813-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Mochly-Rosen D., Newton A., Lee S. H., Koshland D. E., Jr, Cole R. D. Comparison of S100b protein with calmodulin: interactions with melittin and microtubule-associated tau proteins and inhibition of phosphorylation of tau proteins by protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2886–2893. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba K., Mohri T. Different conformation changes induced by calcium and terbium of the porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 10;26(3):711–715. doi: 10.1021/bi00377a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba K., Ohyashiki T., Mohri T. Quantitative analysis of calcium binding to porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. J Biochem. 1983 Feb;93(2):487–493. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba K., Ohyashiki T., Mohri T. Stoichiometry and location of terbium and calcium bindings to porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. J Biochem. 1984 Jun;95(6):1767–1774. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Heidmann O., Lillie J. W., Auffray C., Thomasset M. Sequence of rat intestinal vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein derived from a cDNA clone. Evolutionary implications. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13502–13505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington K. J., Hui A., Hofmann T., Hitchman A. J., Harrison J. E. Porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Molecular properties and the effect of binding calcium ions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington K. J., Kells D. I., Hitchman A. J., Hartison J. E., Hofmann T. Spectroscopic studies on the binding of divalent cations to porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jun;56(6):492–499. doi: 10.1139/o78-076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gérard D., Lemieux G., Laustriat G. Intrinsic fluorescence of S4 and S7 E. coli ribosomal proteins. Photochem Photobiol. 1975 Sep-Oct;22(3-4):89–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1975.tb08818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., James M. N. Structure of the calcium regulatory muscle protein troponin-C at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):653–659. doi: 10.1038/313653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe T., Okuyama T. The amino-acid sequence of S-100 protein (PAP I-b protein) and its relation to the calcium-binding proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 1;89(2):379–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kligman D., Hilt D. C. The S100 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Nov;13(11):437–443. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux B., Baudier J., Gerard D. Tyrosyl fluorescence spectra of proteins lacking tryptophan: effects of intramolecular interactions. Photochem Photobiol. 1985 Sep;42(3):245–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1985.tb08938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mani R. S., Boyes B. E., Kay C. M. Physicochemical and optical studies on calcium- and potassium-induced conformational changes in bovine brain S-100b protein. Biochemistry. 1982 May 25;21(11):2607–2612. doi: 10.1021/bi00540a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mani R. S., Kay C. M. Hydrodynamic properties of bovine brain S-100 proteins. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 30;166(2):258–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mani R. S., Shelling J. G., Sykes B. D., Kay C. M. Spectral studies on the calcium binding properties of bovine brain S-100b protein. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1734–1740. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil J. D., Dorrington K. J., Hofmann T. Luminescence and circular-dichroism analysis of terbium binding by pig intestinal calcium-binding protein (relative mass = 9000). Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;62(6):434–442. doi: 10.1139/o84-059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil J. D., Hofmann T. Tyrosine and tyrosinate fluorescence of pig intestinal Ca2+-binding protein. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):611–615. doi: 10.1042/bj2430611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelling J. G., Sykes B. D., O'Neil J. D., Hofmann T. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies of porcine intestinal calcium binding protein. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2649–2654. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H., Wilchek M., Horwitz J., Billups C. Effects of hydrogen bonding and temperature upon the near ultraviolet circular dichroism and absorption spectra of tyrosine and O-methyl tyrosine derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 25;247(2):572–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaralingam M., Bergstrom R., Strasburg G., Rao S. T., Roychowdhury P., Greaser M., Wang B. C. Molecular structure of troponin C from chicken skeletal muscle at 3-angstrom resolution. Science. 1985 Feb 22;227(4689):945–948. doi: 10.1126/science.3969570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szebenyi D. M., Moffat K. The refined structure of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from bovine intestine. Molecular details, ion binding, and implications for the structure of other calcium-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8761–8777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szebenyi D. M., Obendorf S. K., Moffat K. Structure of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from bovine intestine. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):327–332. doi: 10.1038/294327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


