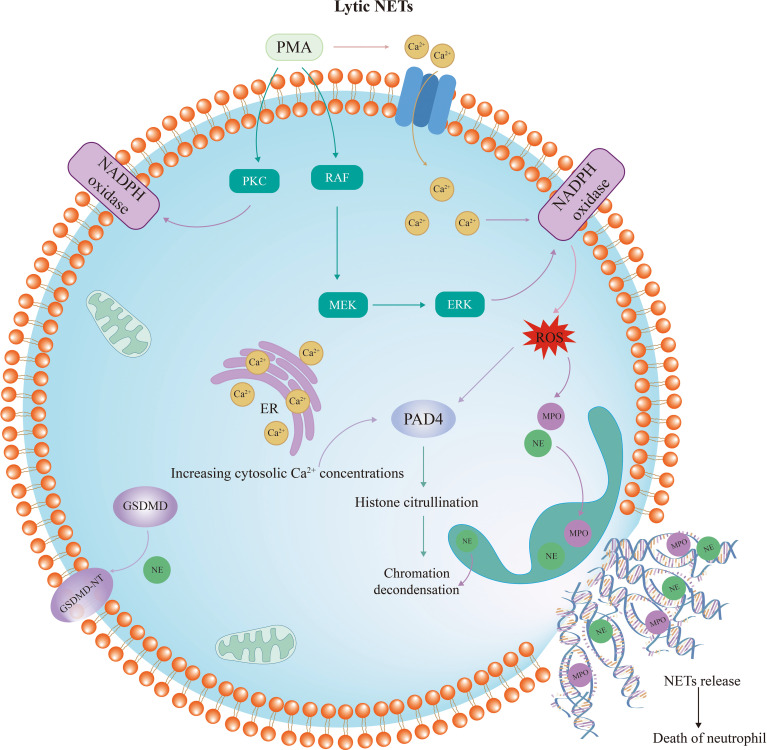
Figure 1.
Diagram of lytic neutrophil extracellular trap formation. The RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and protein kinase C are activated by PMA, resulting in the phosphorylation of NADPH oxidase and ROS formation. This process depends on high calcium concentrations. Subsequently, PAD4 is activated and NE and MPO are translocated from the azurophilic granules to the nucleus. NE, MPO and PAD4 lead to histone citrullination and chromatin decondensation. Upon rupture of the nuclear membrane, the decondensed chromatin enters the cytoplasm and mixes with granular proteins. Finally, the cytoplasma membrane ruptures and the modified chromatin is released from neutrophils, marking the completion of NETosis. PMA, phorbol myristate acetate; PKC, protein kinase C; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NE, neutrophil elastase; MPO, myeloperoxidase; PAD4, peptidyl arginine deiminase-4; GSDMD, Gasdermin D.