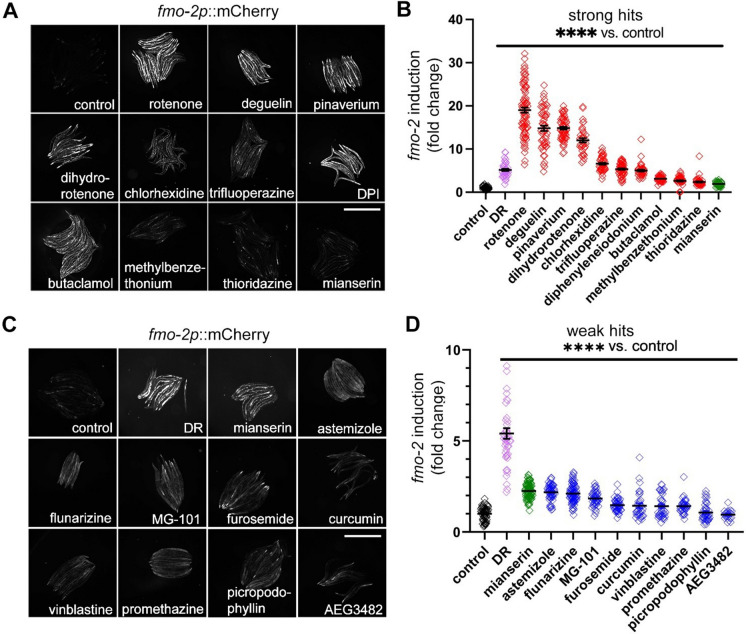
Fig. 2.
Ten strong and nine weak C. elegans fmo-2 inducers are identified from the 80 primary hits that increase stress resistance in mouse fibroblasts. Images and quantification of fmo-2p::mCherry after drug treatments. Strong hits (A–B, red) are defined as drugs that induce fmo-2 more than mianserin (as a cut-off threshold shown in green). Weak hits (C–D, blue) are those agents that induce fmo-2 more than 1.5-fold but less than mianserin dose (green). Dietary restriction (DR) condition is a positive control that induces fmo-2 (purple). Fluorescence intensity in A cannot be compared to intensity in C, since they were performed and analyzed in different experiments with different exposure times. Worms were treated with 1-μM rotenone, 100-μM deguelin, 100-μM pinaverium bromide (pinaverium), 100-μM dihydrorotenone, 30-μM chlorhexidine, 100-μM trifluoperazine, 500-μM diphenyleneiodonium (DPI), 500-μM butaclamol, 100-μM methylbenzethonium, 100-μM thioridazine for strong hits; 100-μM mianserin (~ twofold induction) as a cut-off threshold between strong hits (> twofold induction) and weak hits (< twofold but > 1.5-fold); 1-mM astemizole, 1-mM flunarizine, 1-mM MG-101, 1-mM furosemide, 0.5-mM curcumin, 1-mM vinblastine, 0.5-mM promethazine hydrochloride, 1-mM picropodophyllin, or 1-mM AEG3482 for weak hits. Scale bar, 1 mm. ****Indicates P < 0.0001 when compared to control worms (Welch two-sample t-test, two-sided). Each symbol represents 1 worm, horizontal lines represent means, and error bars represent standard deviation. Each experiment was repeated at least three times. Single dose selected from toxicity tests (Supplementary Table 4) of each drug was used in the experiment