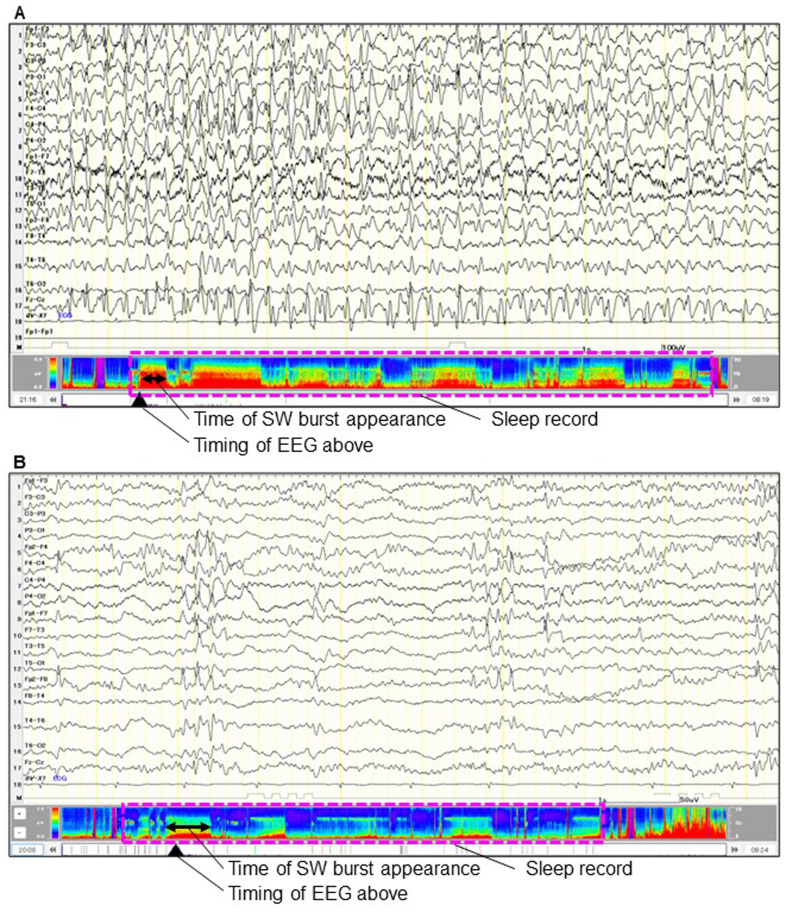
Fig. 1.
(A) Long-term EEG, before the corpus callosotomy (9 years and 7 months of age), revealed a continuous diffuse spike-slow wave burst during non-REM sleep (low frequency filter, 1.59 Hz; high frequency filter, 30 Hz; sensitivity, 20 μV; time constant, 0.3). (B) After the corpus callosotomy (13 years and 7 months of age), the distribution and appearance time of spile-slow wave burst reduced (low frequency filter, 1.59 Hz; high frequency filter, 30 Hz; sensitivity, 10 μV; Tc, 0.3). The density spectral array shows the reduction of the time ratios and powers of the spike-slow wave burst during sleep [pink-dash boxes in (A) and (B)].