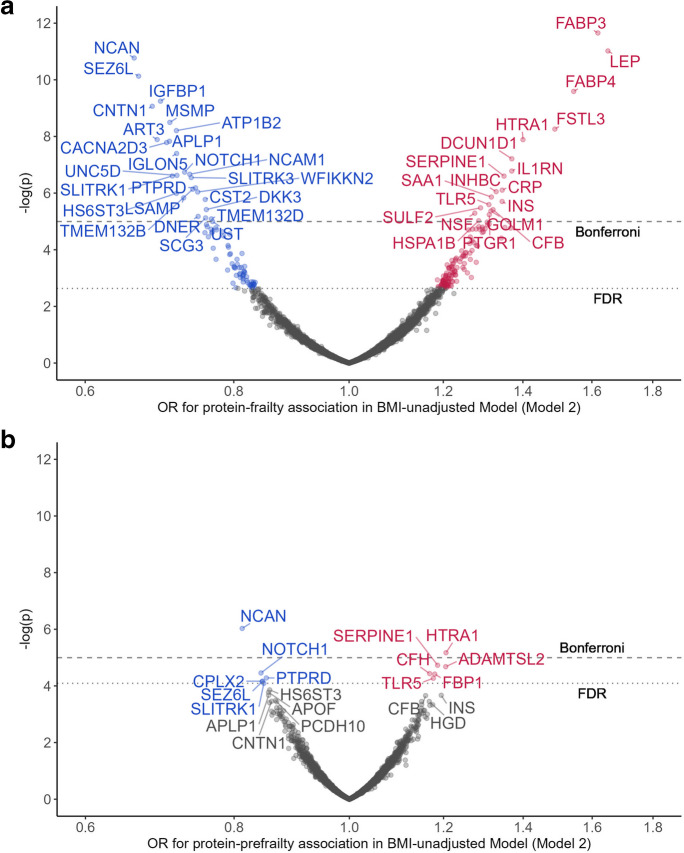
Fig. 1.
Proteins associated with prefrailty (a) and frailty (b) adjusted for age, sex, race-center, education, family income, dietary protein intake, drinking status, smoking status, total cholesterol, estimated glomerular filtration rate, functional limitation, and history of hypertension, diabetes, coronary heart disease, heart failure, stroke, cancer, and lung disease. Top 20 prefrailty-associated proteins were annotated with entrez gene symbol